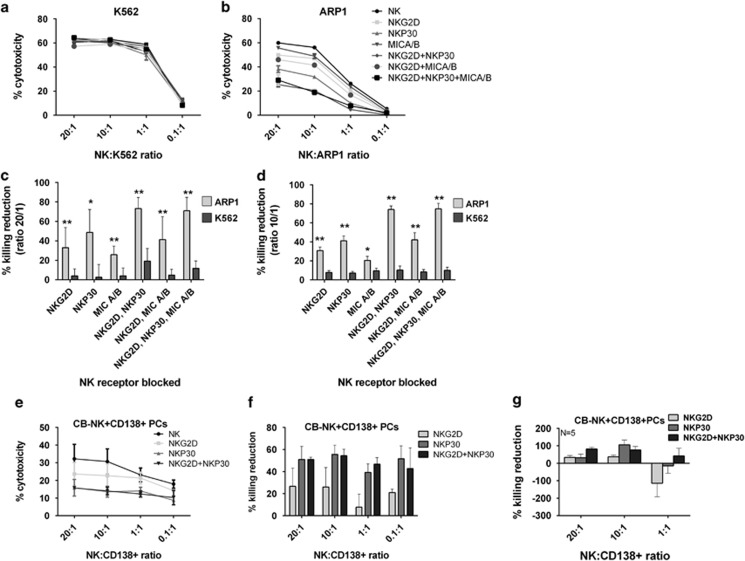
Figure 1.
NKG2D and NKP30 contribute more to the cytotoxicity of MM cells than in K562 cells: (a and b) Cytoxicity assays of CB-NK against K562 (a) and ARP1 (b) cells after blocking NKG2D, NKP30 in CB-NK and MICA/B in target cells. (c and d) Percentage of killing reduction obtained in panels a and b after blocking the receptors. Bars represent mean±S.E.M. values at a effector:target cell ratio 20 : 1 (c) and 10 : 1 (d) (n=8). (e) CB-NK cytotoxicity assay versus primary CD138+ MM cells, adding CB-NK before and after blocking NKG2D, NKP30 and both together. (f) Percentage of killing reduction obtained in panel e after blocking the receptors. (g) Mean values of experiment shown in panels e and f with CD138+ cells from five MM patients. Bars represent mean±S.E.M. *P≤0.05. **P≤0.0001