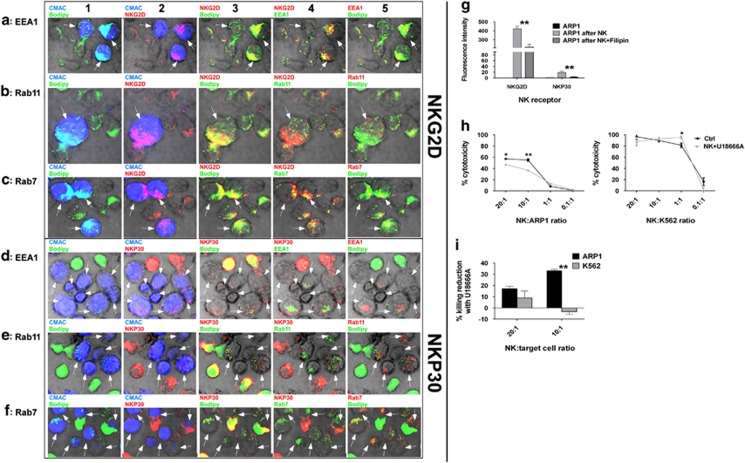
Figure 4.
The transfer of NKG2D and NKP30 into MM cells involves lipid trafficking and the endocytic pathway: Co-localization of NKG2D with (a) EEA1, (b) Rab11 and (c) Rab7 and of NKP30 with (d) EEA1, (e) Rab11 and (f) Rab7 in ARP1 cells after being co-cultured with CB-NK for 20 min. ARP1 cells were stained in blue (CMAC) and CB-NK in green (bodipy), NKG2D and NKP30 are indicated in red. All the images in one row are the same but showing different combinations of colors. In column 1, CMAC and bodipy are shown to indicate ARP1 cells and CB-NK. In column 2, NKG2D or NKP30 and CMAC are shown indicating ARP1 cells with NKG2D or NKP30. In column 3, bodipy in green and NKG2D and NKP30 in red indicate co-localization (yellow) of NKG2D and NKP30 with lipids. In column 4, NKG2D and NKP30 are indicated in red and the endocytic marker in green. In column 5, bodipy in green and the endocytic marker in red indicate co-localization of lipid vesicles with endocytic pathway. Arrows indicate ARP1 cells. (g) NKG2D and NKP30 expression in ARP1 cells alone (ARP1 alone), after being co-cultured with CB-NK for 40 min (ARP1 after NK) and after being co-cultured for 40 min with CB-NK previously incubated with Filipin III (ARP1 after NK+Filipin). (h) CB-NK cytotoxicity reduction versus ARP1 and K562 cells after incubating previously CB-NK with U18666A for 2 h. (i) CB-NK cytotoxicity reduction of results shown in panel h. Bars represent mean±S.E.M. *P≤0.05*. **P≤0.0001