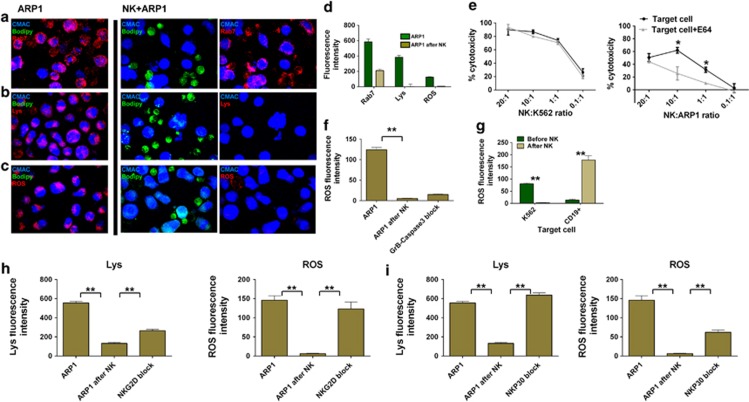
Figure 6.
CB-NK induce lysosomal cell death in MM cells, and NKG2D and NKP30 are involved in this mechanism: (a–d) Analysis of lysosomes (Rab7 and Lyso-trracker: Lys) and ROS production in ARP1 cells before and after co-culture in cell pellet with CB-NK for 40 min. ARP1 cells were labeled in blue (CMAC), CB-NK in green (bodipy) and each marker is indicated in red. (a) Late endocytic and lysosome marker Rab7. (b) Lysosome marker (Lyso-tracker). (c) ROS production. (d) Mean±S.E.M. values of slides analyzed from a to d. Results from a to c were confirmed in three different experiments. (e) CB-NK cytotoxicity reduction after incubating target cells (K562 and ARP1) with E64 (a cysteine cathepsin inhibitor). (f) ROS variation after inhibiting GrB in CB-NK and Caspase-3 in ARP1 cells and co-culturing for 40 min. (g) ROS levels before and after CB-NK exposure for 40 min for K562 cells and CD19+ cells from healthy individuals. (h and i) Variation of lysosome (Lys) and ROS levels after CB-NK exposure for 40 min (ARP1 after NK) and after blocking (h) NKG2D and (i) NKP30 in CB-NK (NKG2D block and NKP30 block). Lysosomes were determined with the Lyso-tracker. Bars represent mean±S.E.M. **P≤0.0001