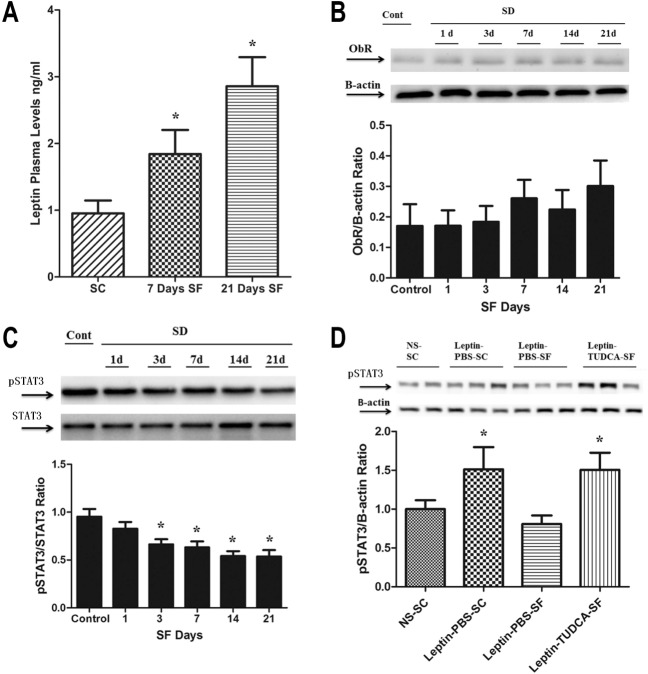
Figure 3.
Sleep fragmentation-exposed mice develop hyperleptinemia over time and attenuation of leptin receptor (ObR) signaling in the hypothalamus. (A) Leptin levels were measured in plasma drawn from fasting mice, and when compared to mice undergoing sleep control (SC) showed increasing levels starting after 1-w exposure to sleep fragmentation (SF), and further increasing at 21 days of SF exposure (n = 11 per group; P < 0.001). (B) Leptin receptor (ObR) expression showed a nonstatistically significant trend toward increases in expression. In parallel, (C) p-STAT3/STAT3 in SF decreased over time when compared with SC (P < 0.03), suggesting reduced ObR receptor signaling. (D) SF mice showed low levels of p-STAT3 expression after leptin injection when compared to baseline (saline injection) or to SC conditions. SF-induced ObR resistance was abrogated when mice were treated with the chemical chaperone TUDCA. PBS, phosphate buffered saline; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid.