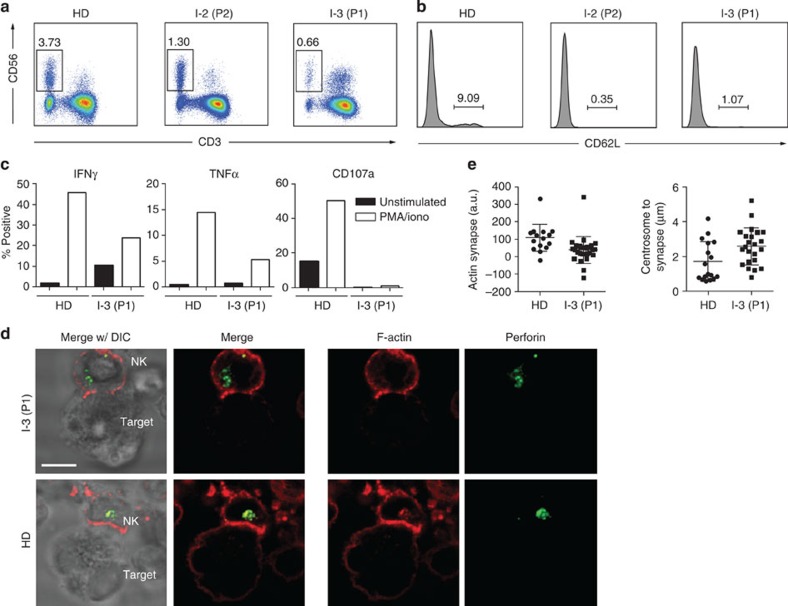
Figure 7. Functional impairment of NIK-deficient NK cells.
(a) Flow cytometric analysis of NK cells in patients and healthy donor. NK cells defined as CD56+CD3−. (b) Histogram of expression of CD62L on NK cells of patients and healthy donor (gated on CD56+CD3− cells). (c) Functional response to PMA and ionomycin of NK cells from NIK-deficient patients and healthy donor. PBMCs from healthy donor (HD, left) or patient 1 (P1, right) were incubated with vehicle control (black) or PMA and ionomycin (white) then fixed, permeabilized and analysed by flow cytometry for intracellular expression of IFNγ, TNFα and CD107a. (a–c) Data represent one experiment. (d) Immunofluorescence analysis of mature immunological synapse formation by NK cells. Immunofluorescence detection of perforin (green) and F-Actin by phalloidin (red) in an NK-cell conjugate from Patient 1 (P1, top panel) or healthy donor (HD, bottom panel). K562 cells were used as target cells. DIC, differential interference contrast. White bar indicates 5 μm. Image is representative of one experiment. (e) Quantification of immunological synapse formation. n=16 (healthy donor) and n=27 (P1) for actin synapse quantification, n=17 (healthy donor) and n=23 (P1) for centrosome to synapse distance quantification; mean ±s.d. shown. Differences are significant as determined by student’s two-sided t-test (P=0.0073 and P=0.0190, respectively).