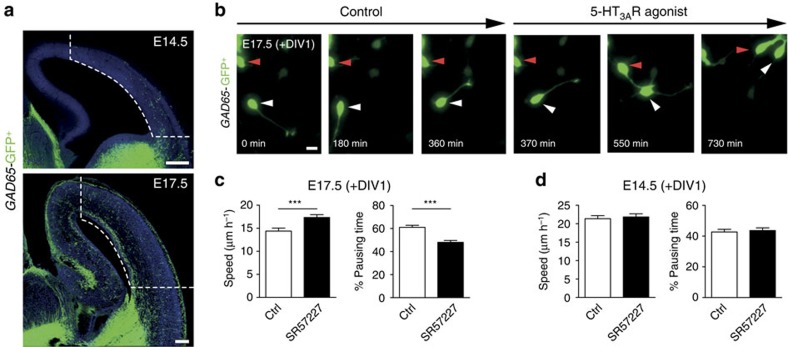
Figure 2. 5-HT3AR activation increases the migratory speed of CGE-derived interneurons (INs) during the phase of cortical plate invasion.
(a) Microdissection of cortical tissue (dotted lines) containing GAD65-GFP+ INs was performed at E14.5 corresponding to the phase of tangential migration or at E17.5 during the phase of cortical invasion. GAD65-GFP+ INs were platted in culture and time-lapse imaging was performed at day in vitro 1 (+DIV1). (b) Illustrative time-lapse sequence showing that GAD65-GFP+ INs (arrowheads) at E17.5 (+DIV1) increase their migration after exposure to the 5-HT3AR agonist SR57227 (100 nM). Cells were tracked during a control period and a drug period of 360 min each. (c, d) Quantification revealed that 5-HT3AR activation significantly increases the migratory speed and decreases the pausing time of GAD65-GFP+ INs at E17.5 (+DIV1; n=156 cells in three independent experiments; c) but not at E14.5 (+DIV1; n=140 cells in three independent experiments; d). ***P<0.001, paired Student’s t-test. Error bars are means±s.e.m. Scale bars: (a) 150 μm; (b) 10 μm.