Table 2.
Power of tests for detecting departures from multiplicative and additive models at the 5% nominal significance level
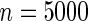 |
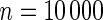 |
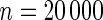 |
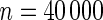 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Power | 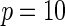 |
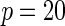 |
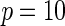 |
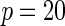 |
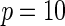 |
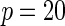 |
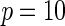 |
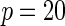 |
| Multiplicative | HL test | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.57 | 0.27 |
| Windmeijer test | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | |
Proposed method 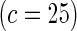
|
0.13 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.12 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.86 | 0.44 | |
Proposed method 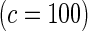
|
0.13 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 0.42 | 0.17 | 0.83 | 0.39 | |
| Additive | HL test | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.41 | 0.13 | 0.76 | 0.23 | 0.99 |
| Windmeijer test | 0.13 | 0.96 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 0.35 | 1 | 0.62 | 1 | |
Proposed method 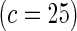
|
0.10 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.50 | 1 | |
Proposed method 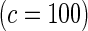
|
0.10 | 0.94 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 0.23 | 1 | 0.45 | 1 | |
The proposed method is evaluated using 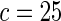 or
or 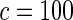 with the corresponding risk regions being defined by the combinations of evenly placed grid points at various upper and lower quintiles of the risk distribution. Results are based on
with the corresponding risk regions being defined by the combinations of evenly placed grid points at various upper and lower quintiles of the risk distribution. Results are based on 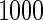 simulated datasets each involving a total of
simulated datasets each involving a total of 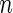 subjects with equal number of cases and controls. In each simulation, data are generated with models involving
subjects with equal number of cases and controls. In each simulation, data are generated with models involving 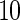 SNPs
SNPs 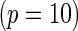 or
or 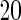 SNPs
SNPs 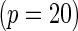 .
.
