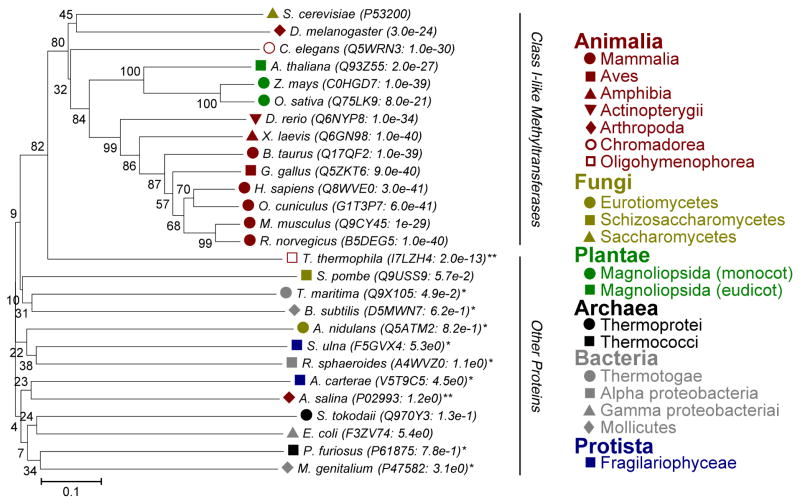
Figure 3. Efm5 is conserved amongst higher eukaryotes.
Phylogenetic tree of Efm5 homologs. Accession numbers and E-values are indicated for each protein. All homologs were mutual best hits except those indicated by an asterisk (*). Double asterisk (**) indicates the organism has the methylation site but not the enzyme potentially due to incomplete genome sequences. Proteins with high similarity are all predicted methyltransferases; those with low similarities are categorized as other proteins.