Figure 7. Multiple thresholds of Wnt/Fzd7/β-catenin activity pattern the endoderm.
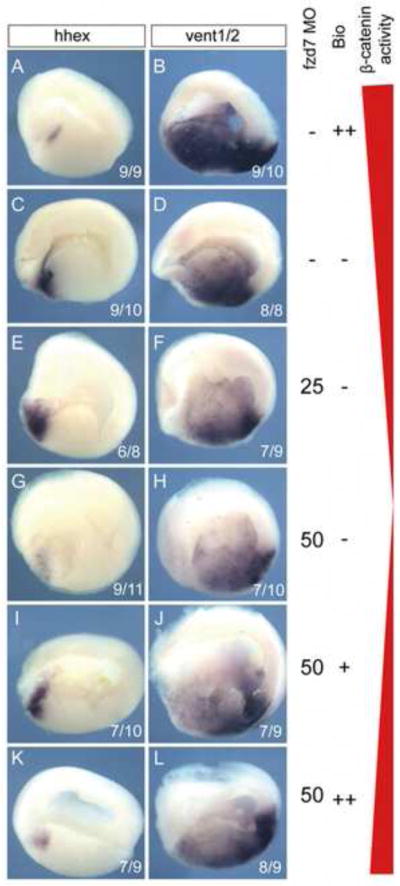
(A–L) Fzd7/β-catenin signaling levels were modulated in a dose response with different combination of fzd7-MOs and/or treatment with BIO, a GSK3 inhibitor that stabilizes β-catenin. In situ hybridization of the foregut marker hhex and the mid/hindgut markers vent1/2 in stage 20 embryos showed that increasing dose of BIO and therefore increasing β-catenin activity decreased hhex while expanding vent1/2 (A, B) relative to untreated controls (C, D). A partial knockdown of Fzd7 (25 ng of fzd7-MOs) resulted in a modest increase in hhex and reduction of vent1/2 (E, F), whereas a complete Fzd7 knockdown by 50 ng of the fzd7-MO caused a loss of hhex, which was not accompanied by an expansion of vent1/2 (G, H). A low dose of BIO (5 uM in I,J) rescued hhex expression in fzd7-depleted embryos (I, J), whereas a higher BIO dose (10 uM) resulted in the foregut adopting a hindgut fate and expressing ectopic vent1/2 (K, L). The number of embryos with the illustrated phenotype is indicated in each panel.
