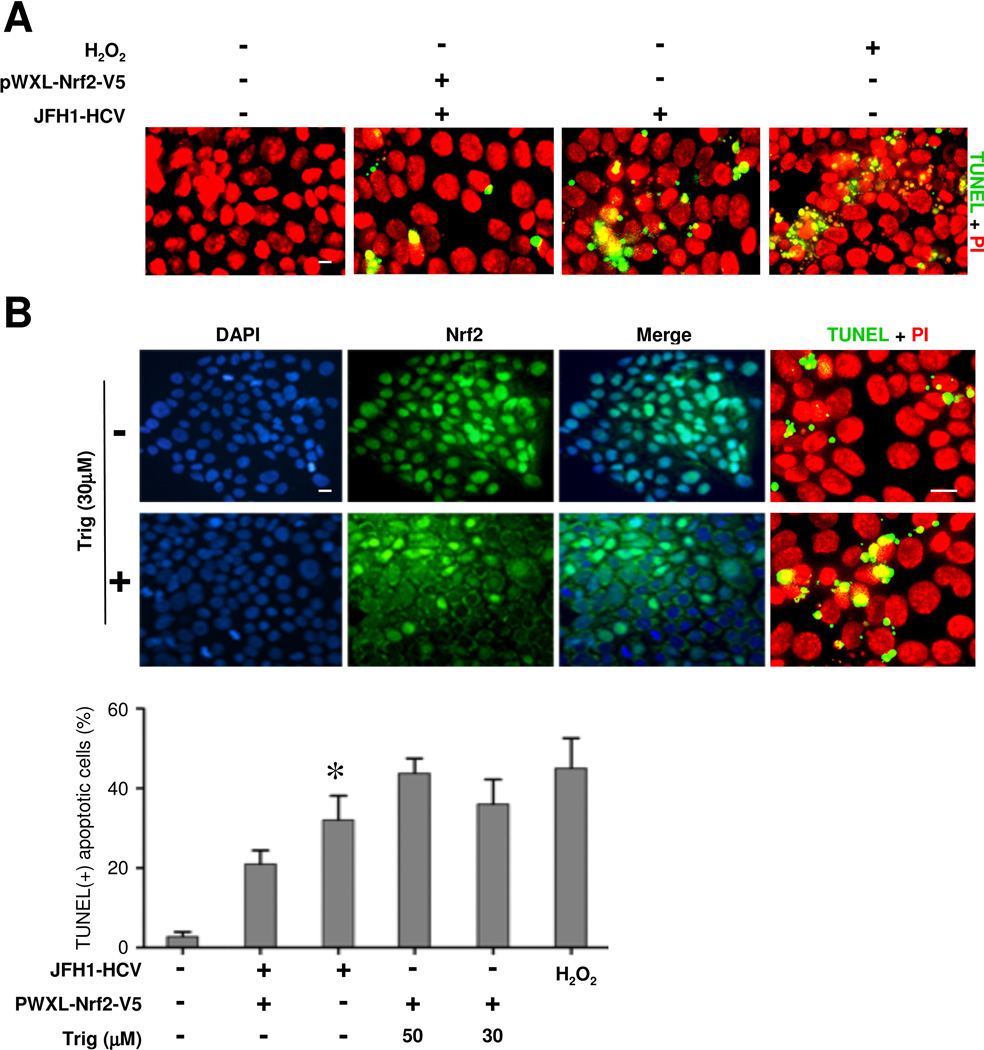
Figure 4. The Nrf2 dependent antioxidant response protects hepatic cells from HCV induced apoptosis.
(A) Huh7.5.1 cells were transfected with the plasmid of pWXL-Nrf2-V5 or empty vector followed by JFH1 HCV or mock infection for 24 h. Cell apoptotic death was probed by immunofluorescence and in situ terminal nick end-labeling (TUNEL, green signals). Nuclei were counterstained with propidium iodide (PI, red signals); Bar = 10 μm. Cells stimulated with hydrogen peroxide (100μM) served as positive control for apoptosis. (B) Huh7.5.1 cells were infected with JFH1 HCV for 48 h in the presence or absence of trigonelline (Trig, 30μM or 50μM), a highly selective small molecule inhibitor of Nrf2. Cells were fixed and subjected to immunofulrescent staining for Nrf2 or TUNEL staining (green signals). Cells were counterstained with DAPI (blue signals) or PI (red signals); Bar = 10 μm. TUNEL-positive cells were counted in five random fields in each culture well, and expressed in percentages of the total number of cells. *P<0.05 versus all other groups (n=3).