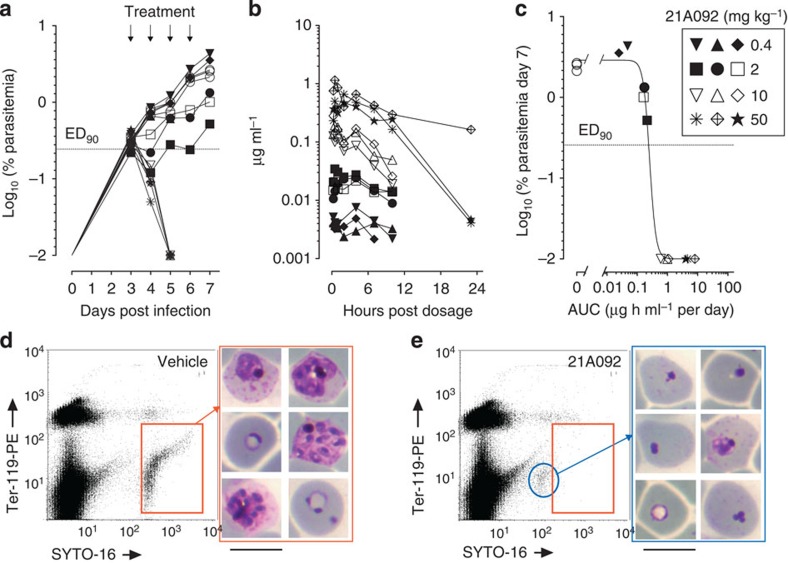
Figure 2. In vivo efficacy of PA21A092 against P. falciparum.
Four indicated doses of PA21A092 were administered orally to groups of three NOD/scid/IL2Rγnull mice each engrafted with human erythrocytes and infected with P. falciparum. The compound was administered starting on day 3 post infection for 4 consecutive days. Parasitemia was assessed each day from day 3 post infection up to 7 days (a). Concentrations of PA21A092 were measured by LC/MS in each mouse at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 7, 10 and 23 h after the first dose (b). The estimated drug exposure necessary to inhibit P. falciparum parasitemia on day 7 post infection by 90% (AUCED90) was 0.24 μg h ml−1 per day−1 (c). Comparison of morphology of parasitized human RBC (as observed in Giemsa-stained thin blood smears prepared on day 7 after infection) in vehicle-treated (d) and PA21A092-treated (e) mice revealed normal stages of parasites in control but erythrocytes with only highly pyknotic staining nuclei fragments in treated mice (scale bars, 10 μm). In a–c, each symbol represents individual mouse with the dose of compound indicated in the inset on the right. Open circles in a are mice treated with the vehicle only.