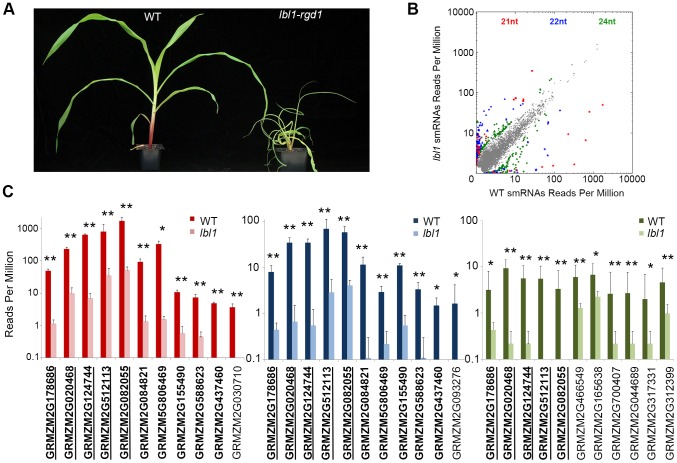
Figure 1. lbl1 affects small RNA biogenesis at select loci.
(A) Compared to wild-type, lbl1-rgd1 mutant seedlings show a reduced stature and develop radial, abaxialized leaves. (B) lbl1 has a relatively subtle effect on the overall small RNA population; in three independent biological replicates 79, 172, and 209 loci generate 21-, 22-, or 24-nt small RNAs, respectively, that are significantly changed (q-value<0.05) at least 2-fold between wild-type and lbl1. Grey dots mark the relative normalized abundance of small RNAs not significantly changed between wild-type and lbl1. Colored dots correspond to significantly changed small RNAs: red, 21-nt; blue, 22-nt; green, 24-nt. (C) Low copy genic regions accumulating significantly fewer 21-nt (left), 22-nt (middle) and/or 24-nt (right) siRNAs in lbl1. Genes marked in bold and underlined show reduced levels for all three siRNA classes. Genes marked in bold show reduced 21- and 22-nt siRNAs. Note that the abundance of 21-nt siRNAs at these loci is generally substantially higher. Values are reported on a log scale and represent the mean normalized read counts (RPM) and standard deviation across three independent biological replicates. * adjusted p-value<0.05; ** adjusted p-value<0.01.