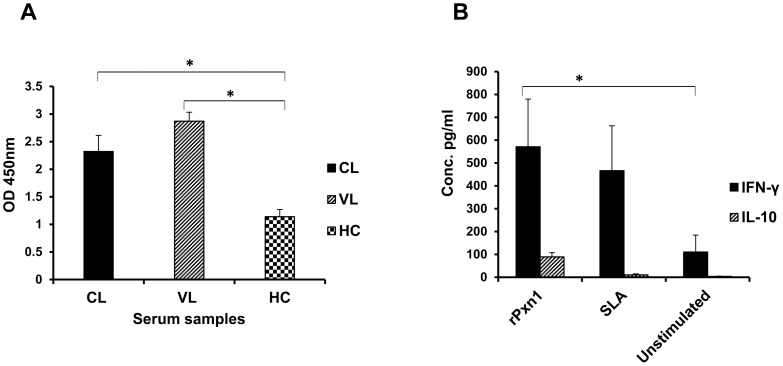
Figure 9. Immunogenicity of rLdPxn1 in cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis patient samples.
(A) The level of LdPxn1-specific total IgG measured from plasma collected from cutaneous (n = 8) and visceral leishmaniasis patients (n = 10) as well as healthy individuals (n = 9) using antibody ELISA. The result was expressed as mean OD450nm and standard error of the mean. Statistical comparison between groups was performed using Mann-Whitney U test. “HC” refers to “Healthy Controls”. (B) The level of IFN-γ and IL-10 in rLdPxn1-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from venous blood of cutaneous leishmaniasis patients (n = 8). Positive and negative control cells were included by stimulation with phytohaemagglutinin (PHA) or adding medium only, respectively. The result represented as mean concentration of IFN-γ and IL-10 and standard error of the mean. Statistical comparison between groups was performed using Mann-Whitney U test. Stimulation with PHA gave 1510.4±67.3 pg/ml IFN-γ and 380.3±77.7 pg/ml IL-10. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference between: CL/VL patient samples and healthy controls (A) or rLdPxn1 stimulated and unstimulated PBMCs from CL patients (B) (p<0.05). The antibody ELISA assay was done in triplicate wells for each patient's serum sample.