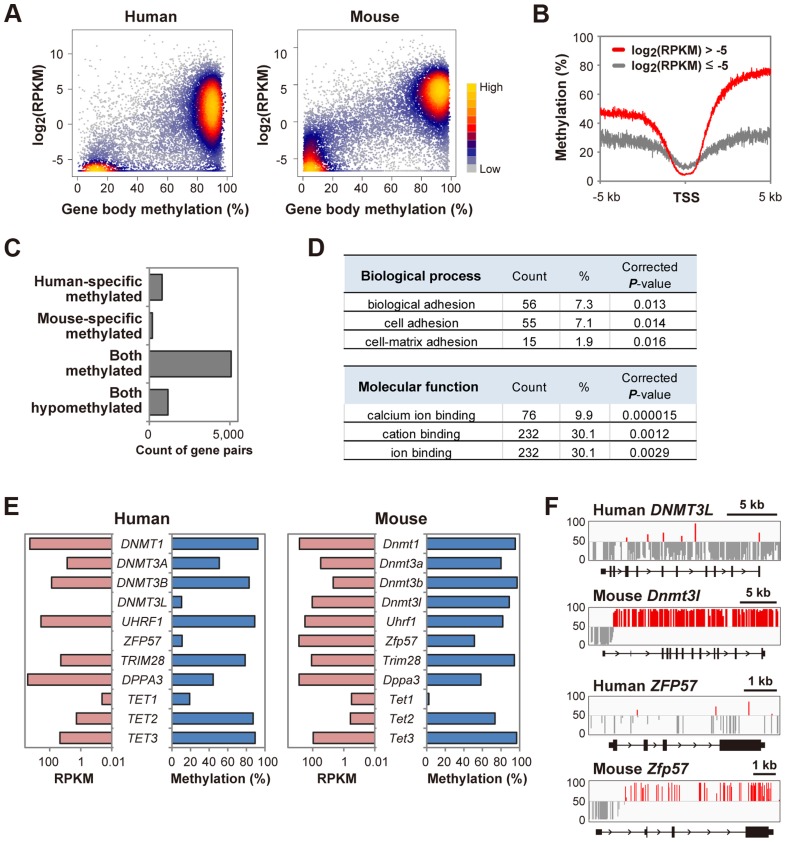
Figure 3. A bimodal gene body methylation pattern associated with transcription in human oocytes.
A, A density scatterplot of gene body methylation levels and transcription levels [43] in human oocytes. The data of mouse oocytes [5], [11] are also shown for comparison. Only genes longer than 5 kb were analyzed. For genes with RPKM less than 0.01, RPKM was set as 0.01. The density is color-coded as indicated. B, Mean methylation levels within 5 kb of transcription start sites (TSS) in human oocytes. Genes (>5 kb) were classified into two groups (log2(RPKM)>−5 and ≤−5). Methylation levels were smoothed using 5 bp non-overlapping sliding windows. C, Conservation of gene body methylation levels between human and mouse oocytes. 783 and 188 genes showed human-specific and mouse-specific gene body hypermethylation, respectively. 5076 and 1151 genes were hypermethylated and hypomethylated in both types of oocytes, respectively. The raw data are shown in S2 Table. D, GO analysis of 783 genes with human-specific gene body hypermethylation. The top three GO terms (biological process and molecular function) are indicated with gene counts, the proportion (%) and BH-corrected P-values. No GO term was enriched in genes with mouse-specific gene body hypermethylation. E, Gene body methylation levels and transcription levels of DNA methylation regulators in human and mouse oocytes. DNMT3L and ZFP57 showed gene body hypomethylation and were not expressed (RPKM<0.01) in human oocytes. DNMT3B (RPKM = 76.0) showed 10-fold higher expression than DNMT3A (RPKM = 7.6) in human oocytes. In contrast, Dnmt3b (RPKM = 4.9) showed ∼6-fold lower expression than Dnmt3a (RPKM = 30.6) in mouse oocytes. F, Methylation patterns at human DNMT3L and ZFP57 loci and mouse Dnmt3l and Zfp57 loci. The vertical line indicates the methylation level (%) and the baseline is set at 50% to highlight unmethylated CpGs. CpGs with>50% and <50% methylation are shown in red and grey, respectively.