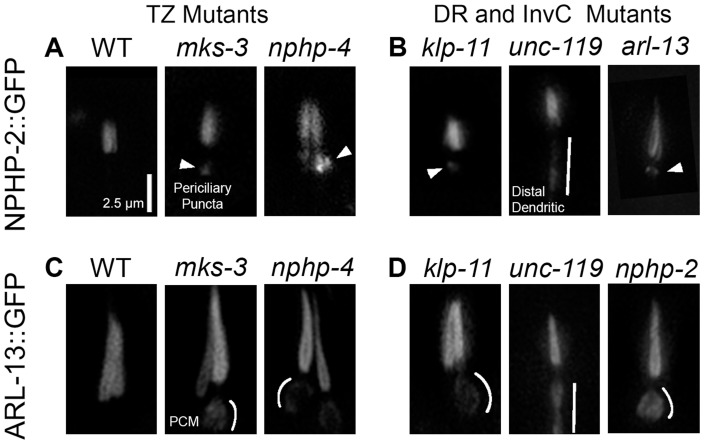
Figure 3. NPHP-2 and ARL-13 do not require TZ-, doublet region-, and InvC-associated genes for ciliary targeting.
(A) In wild type (WT), NPHP-2 is restricted to the proximal cilium. In both nphp-4 and mks-3 mutants NPHP-2::GFP was targeted to the cilium and restricted to the post-TZ proximal cilium. Several NPHP-2::GFP puncta were visible in the periciliary compartment. (B) In doublet region and InvC mutants, NPHP-2::GFP was targeted to the cilium and restricted to the post-TZ proximal cilium in klp-11, arl-13, and unc-119 mutants. arl-13 and klp-11 mutants exhibited periciliary NPHP-2::GFP puncta, and unc-119 mutants exhibited distal dendritic accumulation of NPHP-2::GFP. (C) In WT, ARL-13::GFP localizes to the proximal cilium. In both nphp-4 and mks-3 mutants, ARL-13::GFP was targeted to the cilium and restricted to the post-TZ proximal cilium. ARL-13::GFP also mislocalized to the periciliary membrane compartment in TZ mutants. (D) In nphp-2 and klp-11 mutants, ARL-13::GFP was targeted to the cilium and restricted to the post-TZ proximal cilium. In these mutants, ARL-13::GFP also mislocalized to the periciliary membrane compartment, and in unc-119 mutants, ARL-13::GFP mislocalized to the distal dendrite. Periciliary puncta – arrowheads, periciliary membrane – white arc, distal dendrite/periciliary accumulation – white bar. Periciliary membrane localization was judged by a visible enrichment of ARL-13::GFP on the edges of the periciliary compartment without a concomitant enrichment in the interior lumen of the periciliary region.