Figure 2.
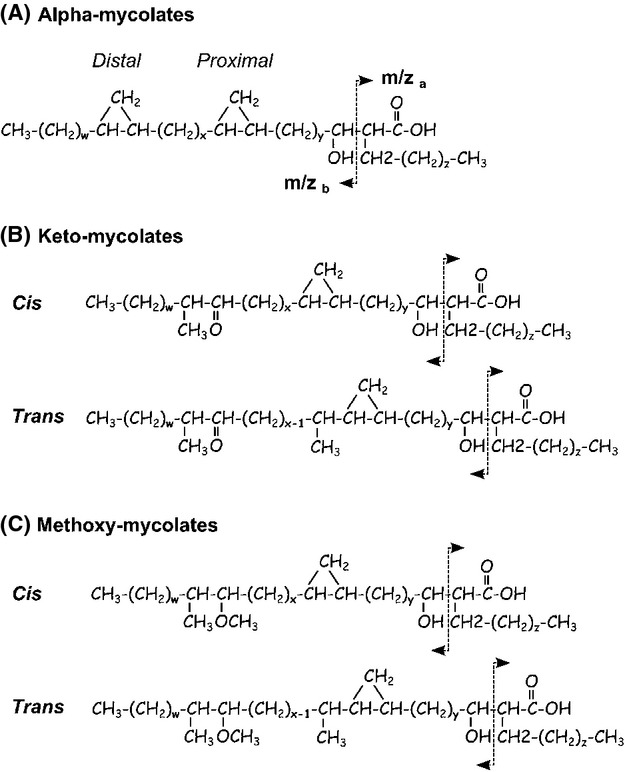
Structure and mass spectrometry fragmentation of the mycolic acid species present in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC). (A) Alpha-mycolates harbor both distal and proximal cyclopropane modifications on their meromycolic chain. (B) Keto-mycolates have a cyclopropane group in the proximal position and a ketone in the distal position of the meromycolic chain. (C) Methoxy-mycolates harbor a cyclopropane group in the proximal and a methoxy group in the distal positions of the meromycolic chain. Cis/trans stereoisomers of keto- and methoxy-mycolic acids (MAs) are distinguished according to the presence (trans) or not (cis) of a methyl group in alpha of the proximal cyclopropane function. MA species vary in length (72 < x + y + z < 89). The arrows indicate the major fragmentation pattern used for mass spectrometry identification of individual species by multiple reaction monitoring (Shui et al. 2012).
