Table 1.
MR Spectroscopy Methods Used to Image Brain Disorders and Metabolites of Interest for Each Disorder
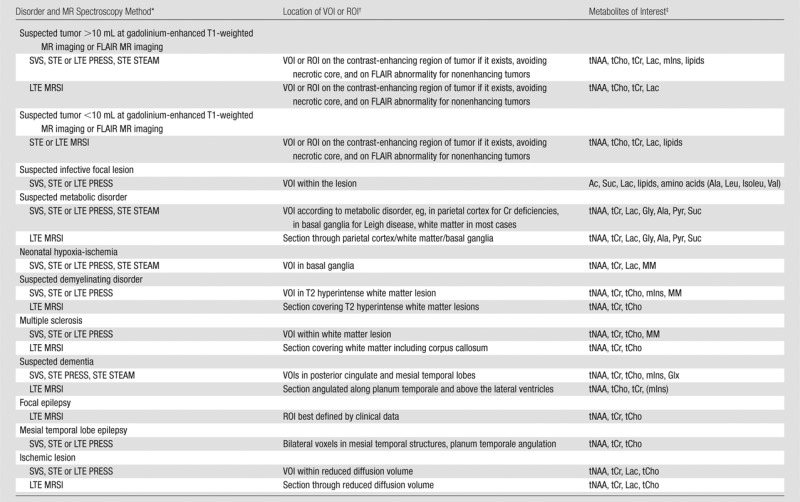
Note.—FLAIR = fluid-attenuated inversion recovery.
Clinically available MR spectroscopy methods that have been widely used for the abnormalities indicated are listed. Short TE is 25–35 msec for PRESS sequence and 20 msec for STEAM sequence. Long TE is 135–270 msec (typically only used for single-voxel spectroscopy); 144 msec is used for Lac inversion, however, precaution is required about chemical shift displacement errors at 3.0 T (38). LTE = long TE, MRSI = MR spectroscopic imaging, STE = short TE, SVS = single-voxel spectroscopy.
ROI = region of interest, VOI = volume of interest.
Note that mIns, a combination of Glu and Gln (Glx), macromolecules (MM), and lipids are detected reliably with short TE sequences, whereas glycine (Gly) is detected reliably with long TE sequences. Ac = acetate, Ala = alanine, Isoleu = isoleucine, Leu = leucine, Pyr = pyruvate, Suc = succinate, Val = valine.
