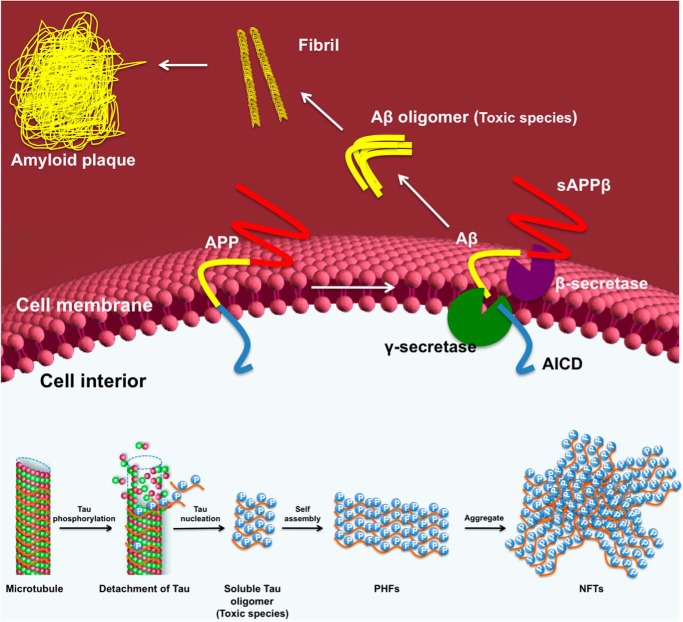
FIGURE 2.
Molecular events giving rise to Aβ and tau pathologies. On the outside of the cell, the combined action of β- and γ-secretase cleavage of the transmembrane APP gives rise to soluble amyloid precursor protein β (sAPPβ) and secreted Aβ, which can then self-associate to form Aβ oligomers. These Aβ oligomers then combine to form higher order amyloid plaques. The APP intracellular domain (AICD) is also liberated by this secretase pathway. On the inside of the cell, phosphorylation of the tau protein promotes its dissociation from microtubules, enabling its aggregation to form competent nuclei or tau oligomers, which can then grow to form larger PHFs. These PHFs aggregate to form the higher order NFTs that are clinically observed in the AD brain.