FIGURE 2.
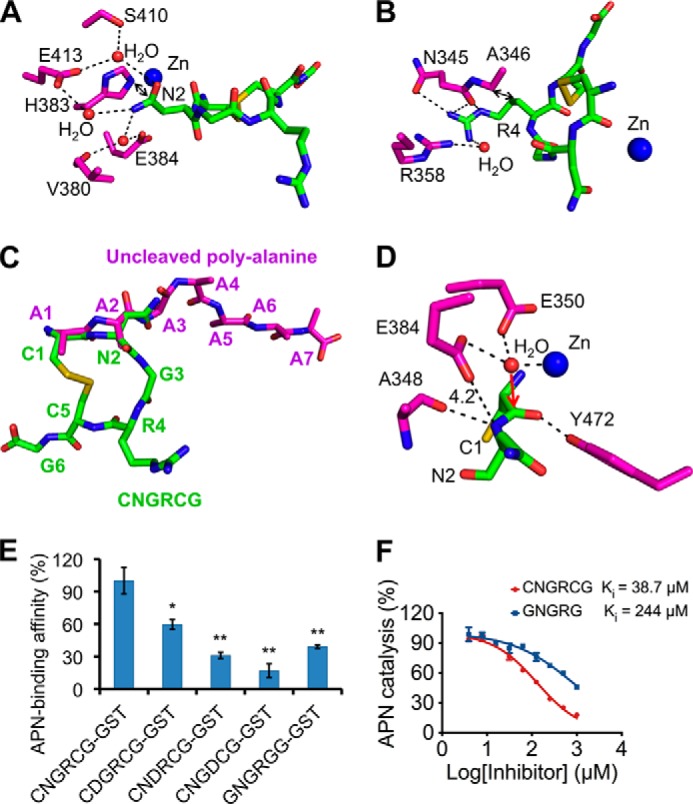
Detailed interactions between pAPN and CNGRCG. A, detailed interactions between pAPN and the side chain of the asparagine in CNGRCG. pAPN residues are in magenta, and CNGRCG is in green. B, detailed interactions between pAPN and the side chain of the arginine in CNGRCG. C, comparison of the conformations of CNGRCG in the crystal of the wild type pAPN-CNGRCG complex and the uncleaved polyalanine peptide in the crystal of mutant pAPN-polyalanine complex (PDB code 4NAQ). D, active site geometry of the pAPN-CNGRCG complex. The presumable scissile peptide bond of CNGRCG has a catalytically inactive conformation, resulting in its leaving nitrogen group being too far away from the proton-transferring pAPN residue Glu-384. Red arrow indicates the potential attack of the scissile peptide bond by the catalytic water at the pAPN active site. Unit of distance is in angstroms. E, pAPN binding by CNGRCG and its mutants. CNGRCG and the mutant peptides were fused to a C-terminal GST tag. The binding affinities of these fusion proteins with pAPN were measured using AlphaScreen protein-protein binding assay. The binding affinity of GST-tagged CNGRCG with pAPN was used as the standard and taken as 100%. Error bars indicate S.E. (compared with the standard two-tailed t test; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; n = 3). F, inhibition of APN catalytic activity by CNGRCG and GNGRG peptides. The catalytic activity of pAPN on Ala-p-nitroanilide in the absence of any inhibitor was taken as 100%. Error bars indicate S.E. (n = 3).
