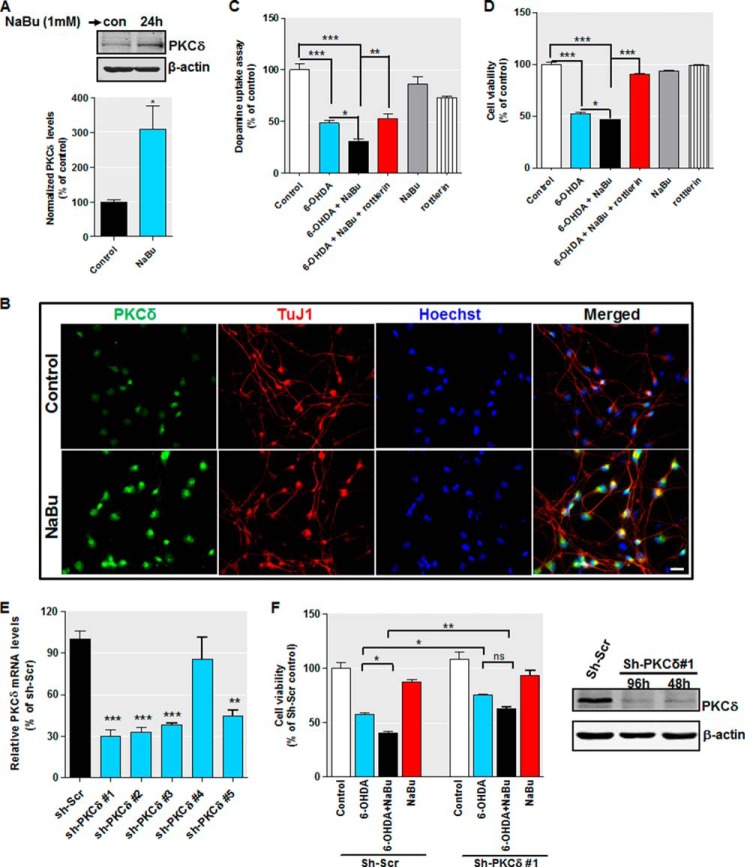
FIGURE 12.
Increased PKCδ potentiates 6-OHDA-induced oxidative damage in differentiated human dopaminergic LUHMES cells. A and B, differentiated LUHMES cells were treated with 1 mm NaBu, and PKCδ expression was analyzed by immunoblot (A) and immunocytochemistry (B). For immunoblot, densitometric quantitation of the ratio of band intensity of PKCδ and β-actin from three independent experiments (means ± S.E.; *, p < 0.05) is shown on the bottom panel. For immunocytochemistry, cells were immunostained for PKCδ (green) and neuron-specific marker β-III tubulin (TuJ1, red), and the nuclei were counterstained by Hoechst 33342 (blue). Images were taken using a Nikon TE2000 fluorescence microscope. Magnification, ×40. Scale bar, 20 μm. Representative immunofluorescence images are shown. C and D, differentiated LUHMES cells were pretreated with or without 1 mm NaBu or 0.3 μm rottlerin for 1 h and then cotreated with 30 μm 6-OHDA for 24 h. After treatment, 6-OHDA-induced oxidative toxicity was measured using the dopamine assay (C) and MTS assay (D). E, LUHMES cells were pre-differentiated for 2 days followed by 2 days of transduction with shRNA lentivirus targeting against human PKCδ (sh-PKCδ) or scrambled lentivirus (sh-Scr). Real time RT-PCR analysis of PKCδ mRNA level was performed. 18 S rRNA level served as internal control. F, left panel, LUHMES cells infected with sh-PKCδ #1 or scrambled lentivirus were pretreated with or without 1 mm NaBu for 1 h and then cotreated with 30 μm 6-OHDA for 24 h. Cell viability was analyzed by MTS assay. All data are expressed as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments and are shown as a percentage of control or scrambled shRNA-infected control cultures. Right panel, LUHMES cells infected with sh-PKCδ #1 or scrambled lentivirus for 48 or 96 h were analyzed for PKCδ expression. Representative immunoblots are shown. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.