Figure 1.
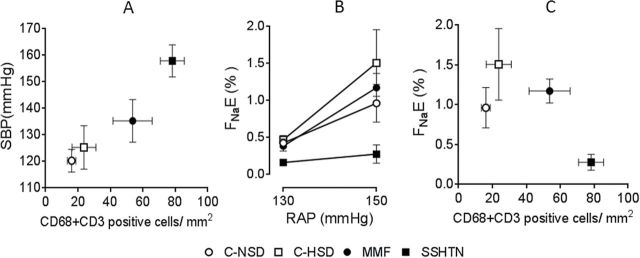
Pressure natriuresis studies in salt-sensitive hypertension induced by transient inhibition of nitric oxide synthase. Control groups received normal (C-NSD; open circles) and high (C-HSD; open squares) salt diet. Experimental groups were studied after 4 weeks of a high salt diet, started after discontinuation of 3 weeks of oral administration of L-NAME given alone (SSHTN; closed squares) or in association with mycophenolate mofetil (MMF; 20mg/kg/day; closed circles). (a) Salt-sensitive hypertension is directly correlated with the intensity tubulointerstitial immune cell infiltration. (b and c) Pressure natriuresis studies are done adjusting renal artery pressure (RAP) by an aortic clamp at 90, 110, 130 and 150mm Hg. (b) Fractional sodium excretion (FNaE) at 150mm Hg of RAP is suppressed in the SSHTN group and restored to normal in the MMF group. (c) Immune cell infiltration (CD3+ cells = lymphocytes; CD68 cells = macrophages) is directly correlated with natriuresis at 150mm Hg RAP. Abbreviation: SBP, systolic blood pressure. Figures made with data from Franco et al.95
