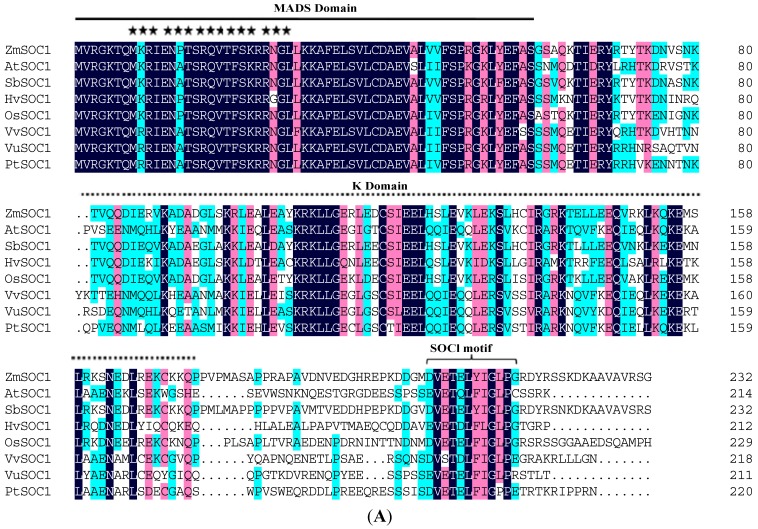
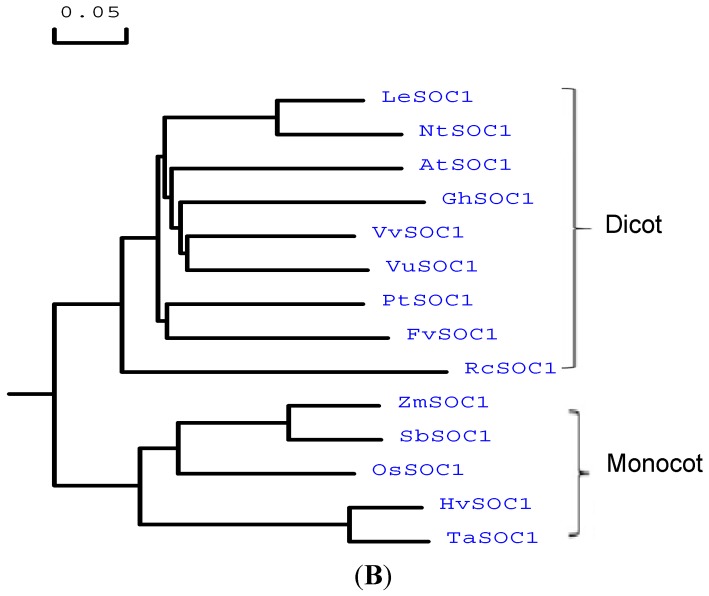
Figure 1.
Bioinformatical analysis of ZmSOC1. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of ZmSOC1 and its homologs from other plant species. The proteins were initially aligned using DNAMAN software. Identical and similar amino acids are shown in black and red shading, respectively. The MADS domain, K domain and SOC1 motif are marked with a solid line, dotted line and brackets, respectively. The locations of potential nuclear localization signals are marked with asterisks within the ZmSOC1 amino acid sequence; (B) Phylogenetic analysis of ZmSOC1 protein and its homologs from various plant species. The DNAMAN software was used for phylogenetic analysis. ZmSOC1 protein could be divided into dicot and monocot clades. The accession numbers of the SOC1-like genes are as follows: Arabidopsis thaliana SOC1: AtSOC1 (NP_182090.1); Hordeum vulgare SOC1: HvSOC1 (BAJ99551.1); Lycopersicon esculentum SOC1: LeSOC1 (NP_001276829.1); Nicotiana tabacum SOC1: NtSOC1 (CAA53782.1); Oryza sativa SOC1: OsSOC1 (NP_001048801.1); Populus tremuloides SOC1: PtSOC1 (AAP46287.1); Ricinus communis SOC1: RcSOC1 (XP_002510866.1); Sorghum bicolor SOC1: SbSOC1 (XP_002465961.1); Vitis vinifera SOC1: VvSOC1 (NP_001267909.1); Fragaria vesca SOC1: FvSOC1 (NP_001266966.1); Vigna unguiculata SOC1: VuSOC1 (BAJ22387.1); Gossypium hirsutum SOC1: GhSOC1 (AEA29618.1); and Triticum aestivum SOC1: TaSOC1 (ABF57922.1).