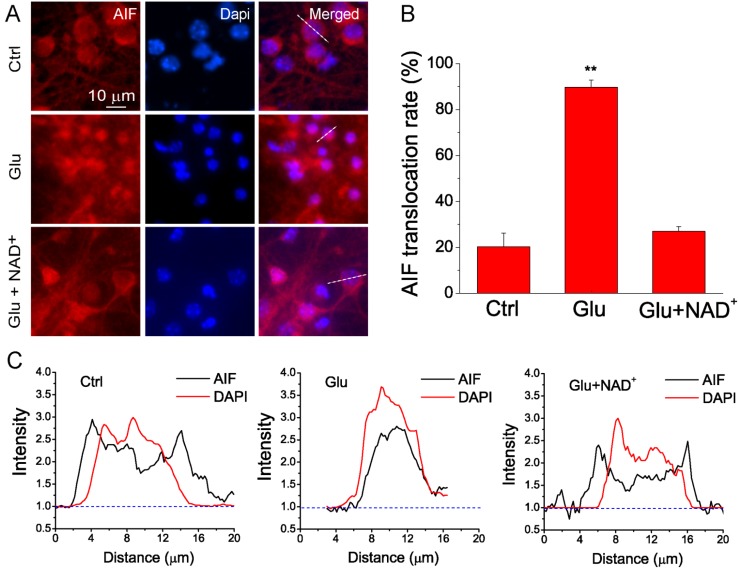
Figure 2.
NAD+ prevents the translocation of apoptotic inducing factor (AIF) from mitochondria to nucleus after glutamate excitotoxicity. (A) Representative images of primary neuronal cultures stained with AIF antibody. Neurons were treated with 100 μM glutamate together with 10 μM glycine in the absence and presence of 15 mM NAD+ for 3 h. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Translocation of AIF from mitochondria to nuclei is illustrated by the overlap of AIF (red) and DAPI (blue) staining; (B) Summary of AIF translocation after glutamate stimulation. Data was quantified by the number of cells with overlap of AIF and DAPI among the total number of cells determined by DAPI staining. Data are shown as mean ± SE; n = 2–3 coverslips per experimental condition from three independent experiments. ** p < 0.01 versus Ctrl and Glu + NAD+, ANOVA test; (C) Line-scan of AIF and DAPI fluorescence from the cells indicated in (A). The fluorescence was normalized to the background. Notice the translocation of AIF after glutamate stimulation and prevention of AIF translocation by NAD+.