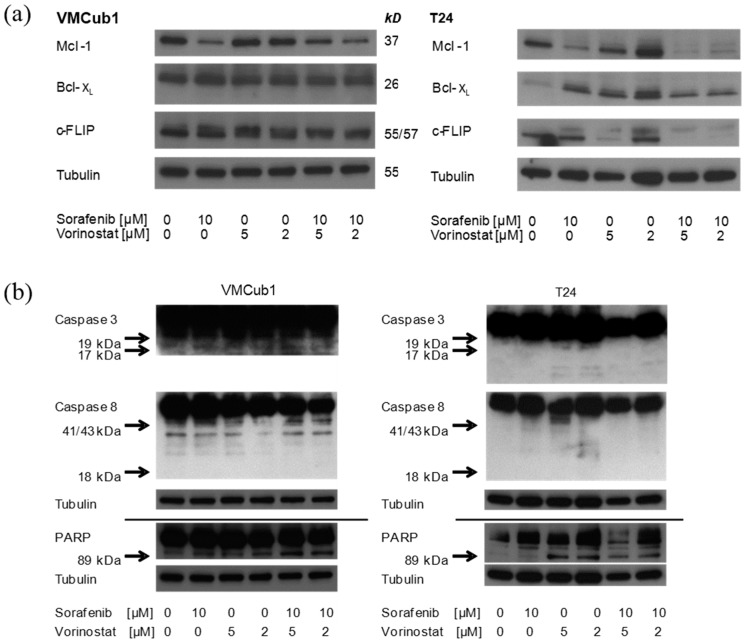
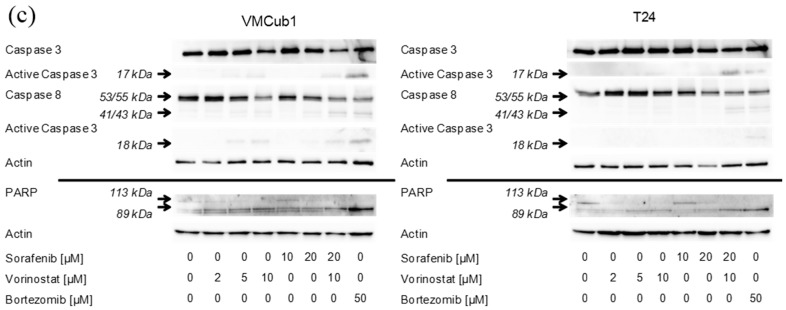
Figure 5.
(a) Effects of sorafenib, vorinostat, and the combination of both compounds on anti-apoptotic factors myeloid cell leukemia 1 (Mcl-1), B-cell lymphoma-XL (Bcl-XL), and c-FLIP. α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. Cells were treated with sorafenib and/or vorinostat for 24 h with the indicated dosages of each compound. α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control; (b) Effects of sorafenib, vorinostat, and the combination of both compounds on cleavage of caspase 3, caspase 8 and poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP). Arrows indicate the expected positions of cleaved products (the blots are deliberately overexposed to visualize these). α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. Cells were treated with sorafenib and/or vorinostat for 24 h with the indicated dosages of each compound; and (c) Effects of sorafenib, vorinostat, and the combination of both compounds (positive control) on cleavage of caspase 3, caspase 8 and PARP using additional anti-bodies against cleaved proteins. Bortezomib was used as positive control as described in [43]. Arrows indicate the expected positions of cleaved products. α-Tubulin was detected as a loading control. Cells were treated with bortezomib, sorafenib, and/or vorinostat for 24 h using the indicated concentrations of each compound.