Figure 3.
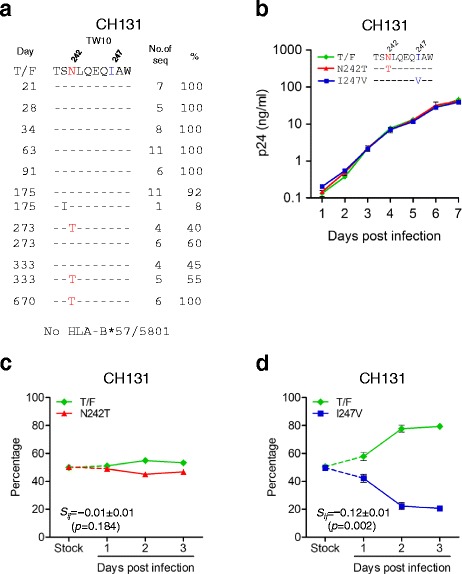
Fitness impact of the T242N mutation and its compensatory amino acid in the transmitted T242N escape mutant. (a) The frequency of the T242N escape mutation in the TW10 epitope was determined by comparing the longitudinal sequences to the CH131 T/F sequence. The days post screening are indicated. (b) The N242T reversion mutation and I247V mutation were introduced into the CH131 T/F viral genome and the replication kinetics of the mutants and their corresponding T/F virus were determined by measuring p24 concentrations in the cell culture supernatants. (c) The relative fitness of the T242N reversion mutant was determined by comparing to the corresponding T/F virus by the PASS fitness assay. (d) The fitness cost of the T242N mutant was determined by comparing the I247V mutant that contained the T242N mutation but not the compensatory isoleucine at position 247 to the T/F virus.
