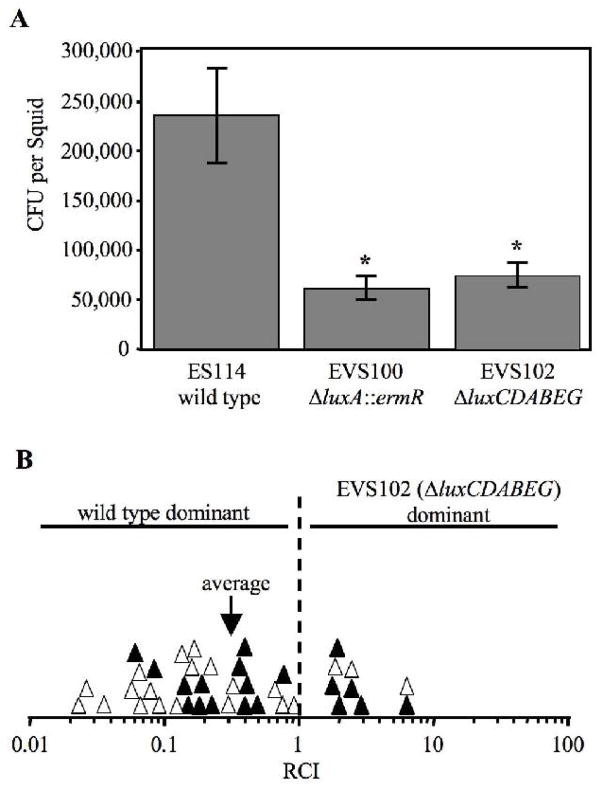
Fig. 7.
Symbiotic colonization of E. scolopes by lux mutants and wild type. a Average colonization levels 48h after inoculation with the indicated strain. Error bars represent standard error (n=17). Asterisks denote a significant (p<0.005) difference from wild type. b Competitiveness of EVS102 (ΔluxCDABEG) when presented in a mixed (~1:1) inoculum with wild type and recovered from squid after 48 h. Either ES114 (solid symbols) or EVS102 (empty symbols) contained pVSV3 (lacZ), which enabled strain identification by blue/white screening after patching on LBS plates supplemented with 50 μg/ml X-Gal. Each symbol represents the RCI determined from one squid, defined as the ratio of EVS102:ES114 in the squid divided by the ratio in the inoculum. An arrow marks the average RCI of 0.32, which was significantly <1 (p<0.01).