Figure 1. CstR forms a modest affinity complex with Cu(I) and metal binding does not negatively regulate cst DNA binding.
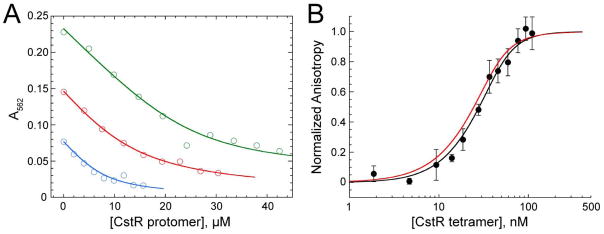
(A) Representative Cu(I)-bicinchoninic acid competition assays with apo CstR. Binding curves were obtained under anaerobic conditions. Open symbols represent the A562 of the Cu(I):BCA2 complex and the solid lines represent the global fitting of three individual experiments to a single-site binding, direct competition model. The global Cu(I):CstR binding constant was calculated to 1.0±0.4×1014 M−1. Green: 29.6 μM Cu(I), 70 μM BCA. Red: 18.9 μM Cu(I), 50 μM BCA. Blue: 10 μM Cu(I), 30 μM BCA. (B) Representative fluorescence anisotropy titration of Cu(I)-bound CstR to a fluorescently labeled cst OP1 DNA fragment. The macroscopic binding constant, Ktet, was determined to be 4.3±1.7×107 M−1. The red line is a simulated curve defined by the binding parameters for apo-reduced CstR (see Fig. 6) under the same solution conditions (Ktet,= 6.3±0.5×107 M−1).
