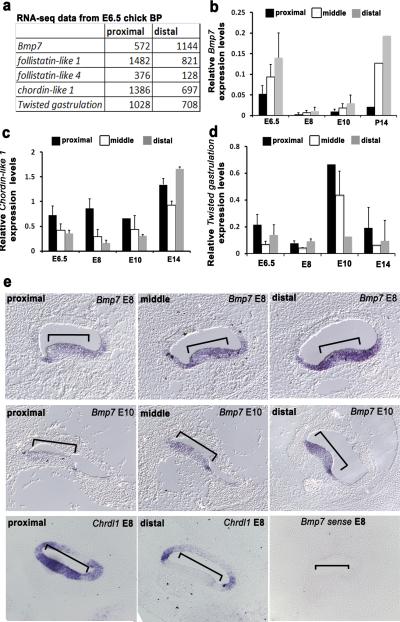
Figure 2. Bmp7 is expressed in a gradient along the tonotopic axis of the BP.
(a)Differential expression of members of the Bmp signalling pathway in proximal and distal regions of the BP at E6.5. Data are presented as the average PMMR (sequences per million mapped reads) forBmp7, Follistatin-like 1& 4, chordin-like 1 and Twisted gastrulation (see text for further details). All experiments were run in triplicate (n=3). (b)Expression of Bmp7 in BP tissue from the indicated regions and time points based onquantitative real-timepolymerase chain reaction (qPCR) data. An increasing proximal-to-distal gradient is present at all four time points. (c)qPCR data for Chordin-like 1 (Chdl1) indicates the presence of a counter (decreasing proximal-to-distal) gradient to Bmp7 between E6.5 and E10.
(d)Twisted gastrulation, which acts to enhance the effects of Chordin-like 1, is also present in a decreasing proximal-to-distal gradient between E6.5 and E10. For b,c and d, data are mean ± sem and n=4 for each developmental age and position along the BP. (e)In situ hybridization for Bmp7at E8 (top), E10 (middle) and Chdl1(bottom)in cross-sections through the BP at the indicated locations. Both Bmp7 and Chdl1are expressed in the developing sensory epithelium of the BP (brackets) and gradients of expression are evident. A sense control for Bmp7(bottom right) was negative.