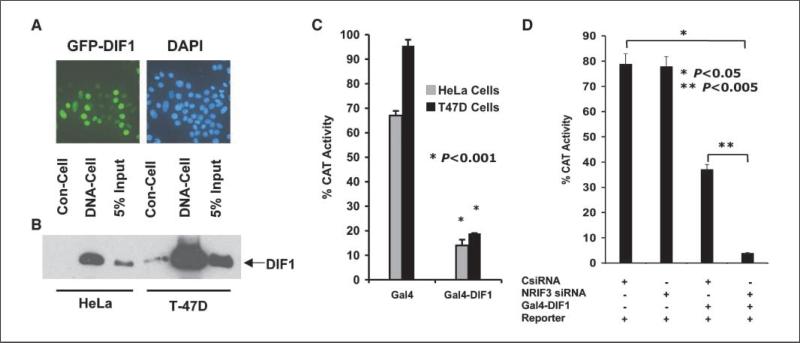
Figure 2.
DIF-1 is a nuclear protein that binds to DNA-cellulose and mediates transcriptional repression. A, GFP-DIF-1 expressed in T-47D cells localizes to the nucleus. B, HeLa and T-47D cells expressing FLAG-HA tagged DIF-1 were lysed in 0.3 mol/L KCl buffer. The supernatants were bound to FLAG antibody beads and then eluted with 3× FLAG peptide. Samples were incubated with DNA-cellulose (DNA-Cell) or with cellulose control (Con-Cell), and after washing, the cellulose beads were analyzed for DIF-1 by Western blotting with FLAG antibody. The input represents 5% of the sample before the binding assay. C, HeLa or T-47D cells were transfected with 100 ng of the pG5-SV-BCAT reporter along with 200 ng of vector expressing Gal4-DIF-1 or 150 ng (equal molar amount of plasmid) expressing only the Gal4 DBD. CAT activity was analyzed 30 h later. Gal4-DIF-1 represses the Gal4-CAT reporter in both cell types. D, HeLa cells were transfected as indicated with an NRIF3 siRNA (25 nmol/L) or a control-siRNA (25 nmol/L). Thirty hours later, the cells were transfected with 100 ng of pG5-SV-BCAT alone and with 50 ng of the Gal4-DIF-1 vector. CAT activity was determined 30 h later.