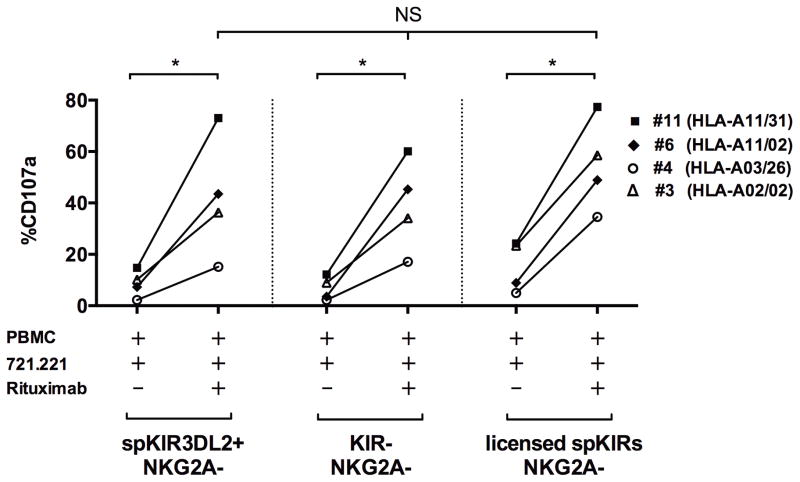
Figure 4. Hypo-responsive NK cells exclusively expressing KIR3DL2 are activated by rituximab.
Shown is the degranulation (CD107a) response by NK cells exclusively expressing KIR3DL2 induced by 721.221 B-lymphoblasts with or without rituximab. CD107a results from 4 subjects were aggregated: subject #11 (HLA-A11/31), #6 (HLA-A11/02), #4 (HLA-A3/26), and #3 (HLA-A02/02). Similar to the KIR−NKG2A− (shown) and unlicensed spKIR+NKG2A− (not shown) NK cells, NK cells exclusively expressing KIR3DL2 were hypo-responsive to 721.221 B-lymphoblast tumor cells alone, but degranulated after the addition of rituximab, comparable to the licensed NK cell subset. Statistical comparisons were made using the Mann-Whitney and Kruskall-Wallis tests, with *P<0.05. The presence of the HLA-A11 (subject #11, #6) or -A3 (subject #4) ligand did not influence the antibody-dependent activation of the spKIR3DL2+ NK cell subset.