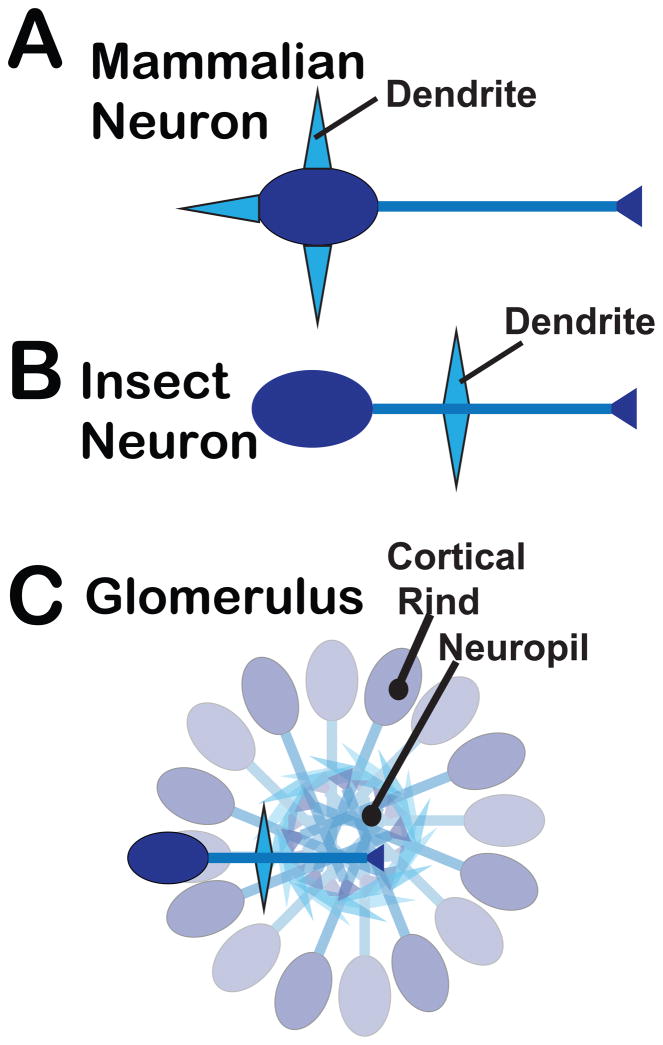
Figure 2. The morphology and organization of mammalian and insect neurons.
A canonical mammalian (A) and insect neuron (B) are indicated, highlighting differences in the location of dendrites: on the cell body of mammalian neurons versus a single process emanating from the soma of insect neurons that also gives rise to the axon. This morphology allows the characteristic organization of insect neurons into glomeruli (C), or larger but similarly organized ganglia, which include a cortical rind and neuropil as indicated.