Figure 2.
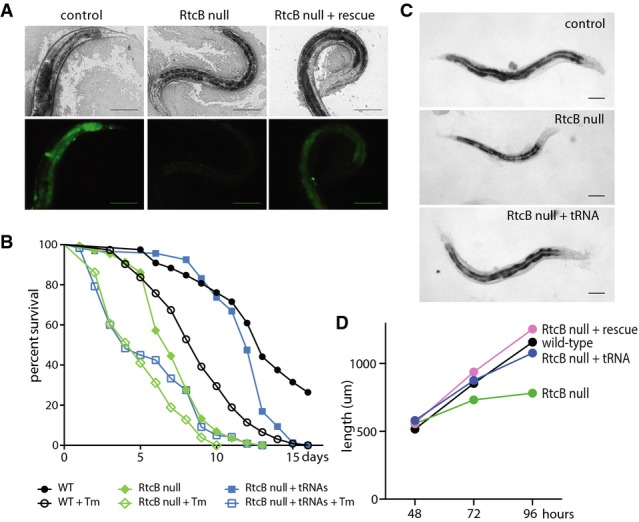
RtcB is required for survival under conditions of ER stress
A Brightfield (top panels) and fluorescence (bottom panels) images of animals expressing the Phsp-4::GFP reporter. Animals were exposed to tunicamycin before imaging. Control animals (RtcB/+) exhibit strong GFP expression in multiple tissues; RtcB mutants fail to express GFP (faint signal is gut autofluorescence); expression of RtcB in the intestine of RtcB mutants rescues GFP expression specifically in intestinal cells. Scale bars, 100 μm.
B Survival curves for wild-type animals (black), RtcB mutants (green), and RtcB mutants expressing pre-spliced tRNAs (blue). Filled symbols indicate normal growth conditions, and unfilled symbols indicate growth on tunicamycin. y-axis indicates the percentage of worms that survived. x-axis indicates the number of days after L4 stage.
C Age-matched wild-type, RtcB mutant, and RtcB mutant worms expressing pre-spliced tRNAs. Scale bars, 100 μm.
D Average length of wild-type (black), RtcB mutants (green), genomic rescued RtcB mutants (pink), and RtcB mutants expressing pre-spliced tRNAs (blue) at 48, 72, and 96 h after eggs were laid. N = 20 per genotype.
