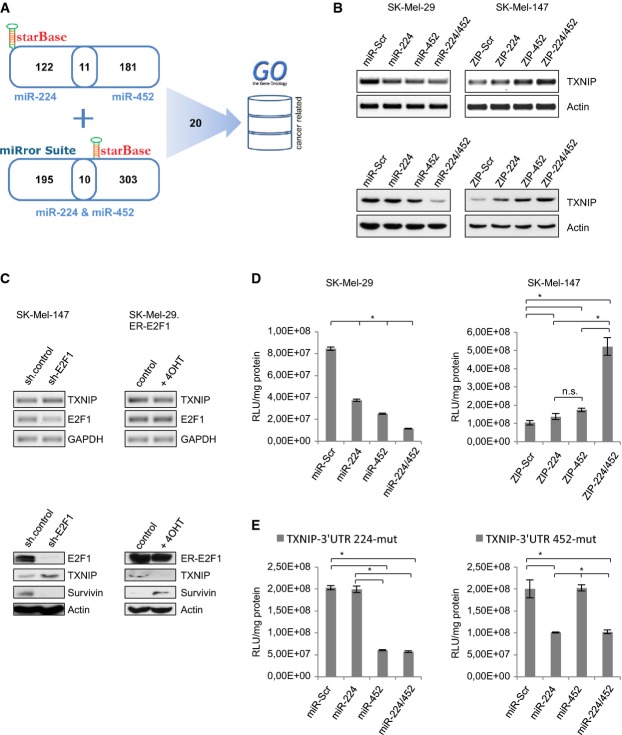
Figure 4.
Identification of TXNIP as miR-224/452 target
A Scheme of target prediction for miR-224/452.
B MiR-224/452 regulates TXNIP. Overexpression of miR-224/452 in SK-Mel-29 resulted in less TXNIP expression, while inhibition of the endogenous miRNAs in SK-Mel-147 induced TXNIP. Transcript and protein levels were determined using actin as a control.
C Knockdown of E2F1 in SK-Mel-147 increases and E2F1 activation by addition of 4-OHT in SK-Mel-29.ER-E2F1 reduces TXNIP expression on RNA and protein level. GAPDH and actin served as loading controls.
D Luciferase reporter assay revealed a direct regulation of TXNIP by miR-224 and miR-452. Co-transfection of pMiR-Report-3′ UTR(TXNIP) and miR-224/452 plasmids in SK-Mel-29 results in less luciferase activity (in comparison with miR-Scr). Promoter activity is upregulated in miRZip-transfected SK-Mel-147.
E Mutation of miR-224/452 binding sites in the TXNIP-3′ UTR completely abolishes their repressive effects. Luciferase activity was measured after co-expression of pMiR-Report-3′ UTR(TXNIP-224-mut) or -(TXNIP-452-mut) with miR-224/452 in comparison with miR-Scr in SK-Mel-29.
Data information: Bar graphs are represented as means ± SD, n = 3, *P ≤ 0.05, two-sided Student's t-test.