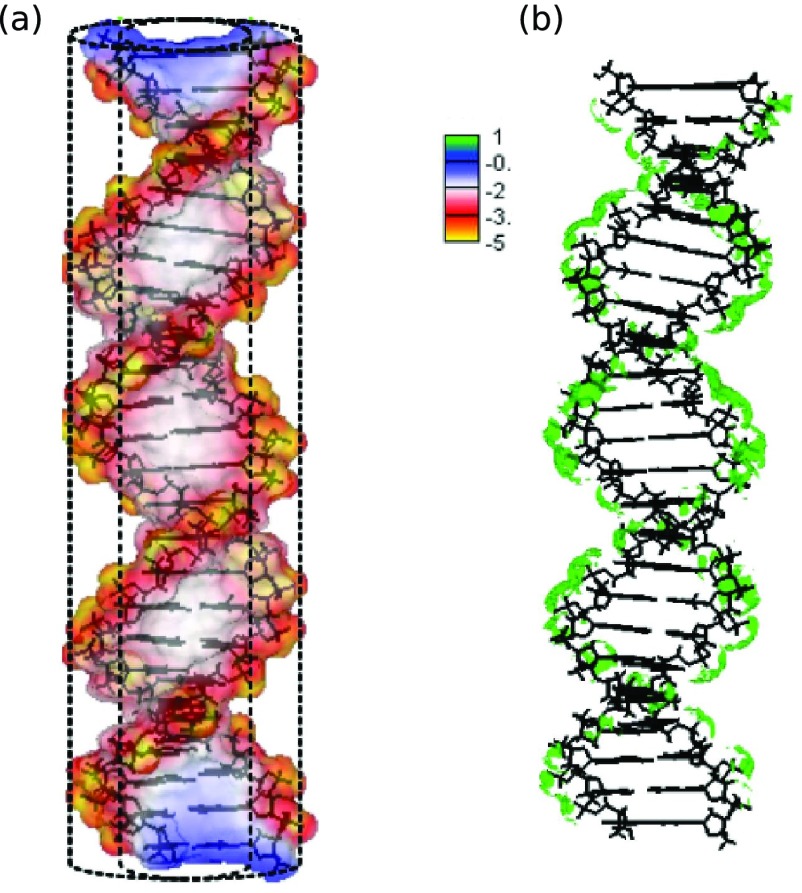
FIG. 1.
The electrostatic potential (in 1/(βe), where ) of a 24 base pair ideal Watson-Crick B-DNA helix is mapped on its solvent-excluded molecular surface (a). The 6M Na+ iso-concentration contour around the same B-DNA helix is shown in green (b). The adaptive Cartesian grid-based Poisson-Boltzmann solver (CPB)79,80 is used with the following settings: the interior and exterior dielectric constant are set to 1 and 80, respectively, the solution temperature is 298.15 K and the NaCl concentration is 0.1M. An ion exclusion thickness of 2 Åis employed. A simplified B-DNA charge model, where each non-bridging phosphate oxygen is assigned a charge of −0.5e and all other atomic charges are set equal to zero, is employed to showcase sequence independent electrostatic features of the classical B-DNA.