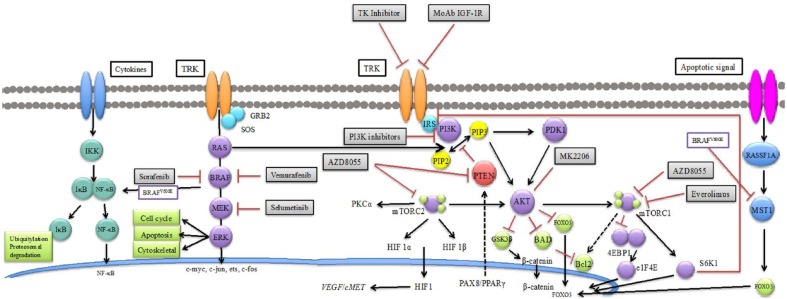
Figure 2.
Main oncogenic pathways and targeted therapies in thyroid carcinoma. HIF1, hypoxia-inducible factor 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase; PKC, protein kinase C; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; IKK, IB kinase; IB, inhibitor of kappa; B NF-KB, nuclear factor KB; TRK, Receptor thyrosine kinase; Grb2, Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; SOS, son of sevenless; RAS, Rat sarcoma; BRAF, B-type rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinases; IGF-1R, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor; IRS, Insulin receptor substrate; PI3K, phosphatidylinositide 3-kinasen; PKC, protein kinase C; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin;
HIF1, hypoxia-inducible factor; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; MET, mesenchymal epithelial transition; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorn; PDK1, Phosphoinositide dependent kinase-1; FOXO3, forkhead box O3; BAD, Bcl-xL/Bcl-2-Associated Death Promoter Bcl2, B-cell lymphoma 2; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta 4EBP1: 4E-binding protein 1 EIF4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; S6K1, S6 kinase 1; RASSF1A, Ras association domain family 1 isoform A; MST1, macrophage stimulating protein.