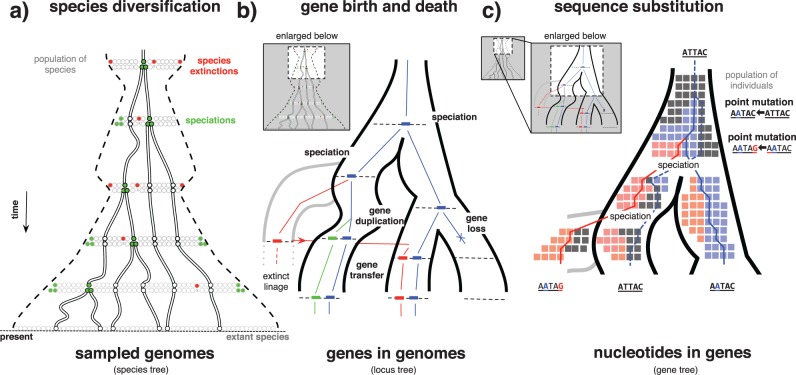
Figure 1.
A hierarchy of evolutionary processes contribute to sequence evolution. a) Individual species (circles) and their genomes evolve among a population of species, according to a diversification process consisting of speciation (light gray, green online) and extinction (dark gray, red online) events. The variation in the number of species existing at any given time is indicated by the dashed contour. When attempting to infer the species tree typically only a fraction of existing species (gray and black circles on dashed line) are sampled (black circles). b) Inside each genome, each gene evolves according to gene duplication, loss, and transfer events. c) Individual sites evolve through point mutations. Processes at the gene and site level are played out at the population level, where changes fix or are lost.