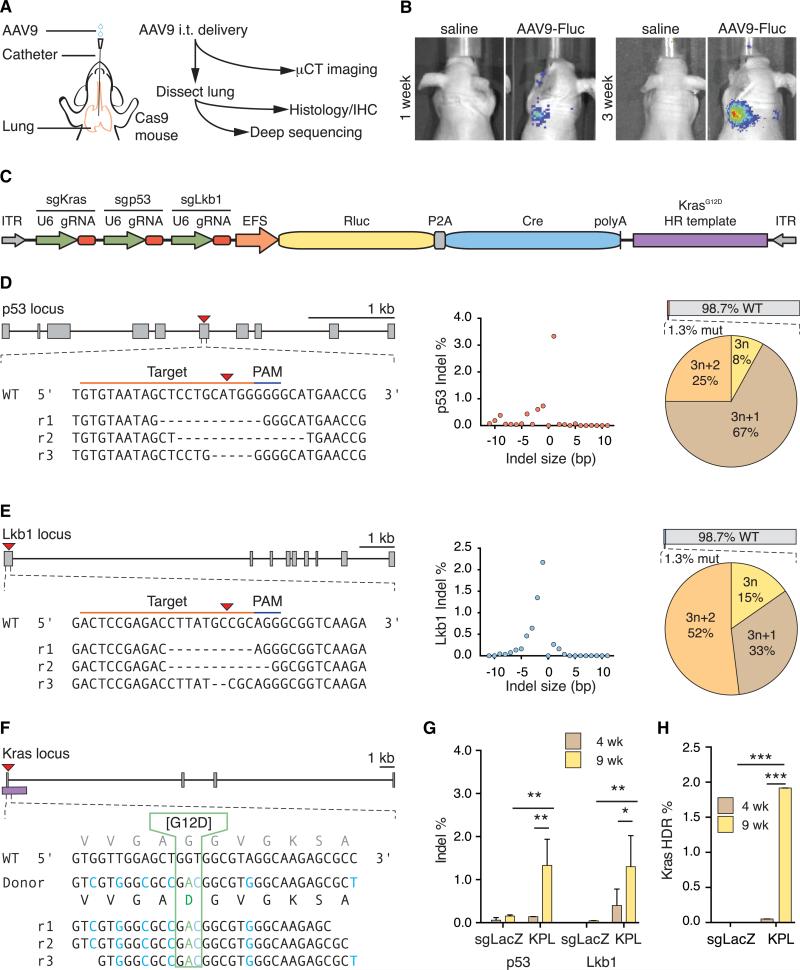
Figure 4. In Vivo AAV9-KPL Delivery and Mutation Analysis.
(A) Schematic of intratracheal (i.t.) delivery of AAV9 into the lung of a Cre-dependent Cas9 mouse and experimental flow.
(B) Luciferase imaging of nude mice injected with either AAV9-Fluc or saline, showing efficient AAV9-mediated expression in vivo in the lung.
(C) Schematic of the AAV-KPL vector.
(D and E) (Left) sgRNA designs for targeting the mouse p53 (D) and LKB1 (E) loci and representative Illumina sequencing reads (rn) from Cre-dependent Cas9 mice injected with AAV9-KPL, showing indel formation at the target site. (Middle) Size distribution of indels found at the target site. (Right) Indel analysis from whole lung (top) and the phase characteristics of edited alleles (bottom). p53 and LKB1 loci scale bars, 1 kb.
(F) sgRNA and HDR donor design for targeting the mouse KRAS locus for G12D incorporation and representative Illumina sequencing reads (rn) from Cre-dependent Cas9 mice injected with AAV9-KPL. Green text indicates the G12D mutation, whereas blue text indicates the intended synonymous mutations, showing successful generation of the KRASG12D mutation. KRAS locus scale bar, 1 kb.
(G) p53 and LKB1 indel analysis of whole lung from Cre-dependent Cas9 mice injected with either AAV9-KPL or AAV9-sgLacZ, showing significant indel formation only in AAV9-KPL-injected mice. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005.
(H) KRASG12D mutation analysis of whole lung from Cre-dependent Cas9 mice injected with either AAV9-KPL or AAV9-sgLacZ, showing significant G12D incorporation only in AAV9-KPL-injected mice. The data are plotted as the mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.0005.
See also Figures S3, S4, and S5.