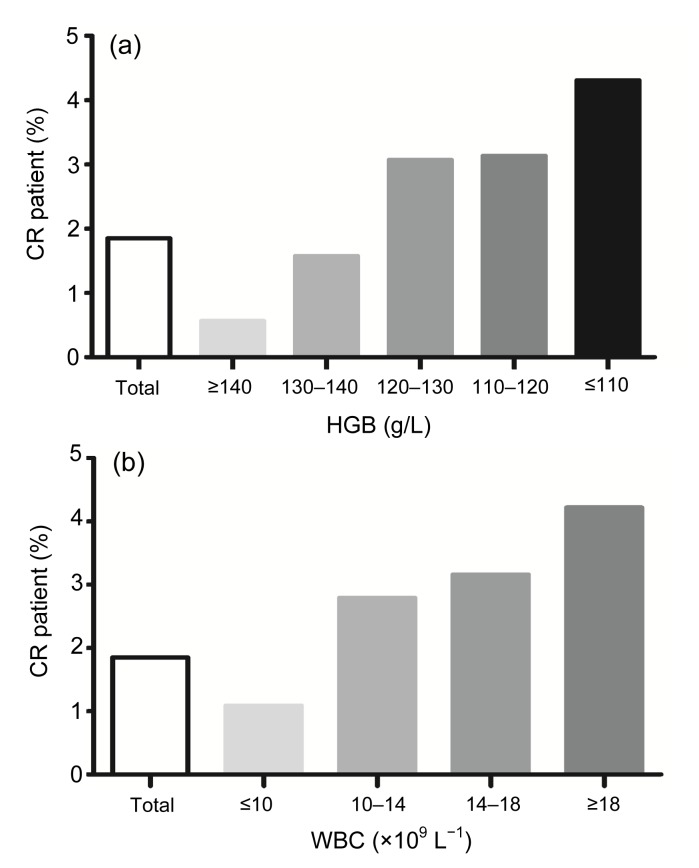
Fig. 1.
Relations between cardiac rupture (CR) and anaemia (a) and white blood cell (WBC) levels (b)
(a) CR incidence increases with the decline of hemoglobin (HGB): 22 (0.56%), 35 (1.57%), 47 (3.07%), 29 (3.13%), and 45 (4.31%) for ≥140, 130–140, 120–130, 110–120, and ≤110 g/L HGB, respectively. (b) CR incidence increases with the increase of WBC levels: 63 (1.09%), 75 (2.79%), 28 (3.16%), and 12 (4.22%) for ≤10×109, 10×109–14×109, 14×109–18×109, and ≥18×109 L−1 WBC, respectively