Fig. 1.
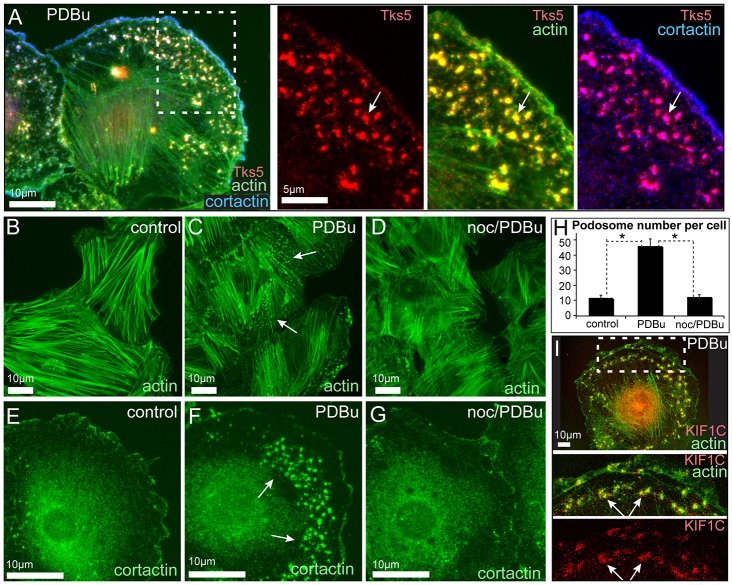
Podosome formation in A7r5 cells requires MTs. (A) Visualization of podosomes in a PDBu-treated A7r5 cell by expression of Tks5–GFP (red) and immunofluorescence detection of actin (phalloidin, green) and cortactin (blue). The boxed region from the overview (left) is enlarged on the right and shows Tks5-positive podosomes and their colocalization with actin and cortactin. Maximal-intensity projection of a confocal stack. Arrows, podosomes. (B–G) Wide-field fluorescence microscopy of actin (phalloidin, B–D) and cortactin (E–G) in A7r5 cells. Multiple podosomes are spread throughout a cell after 40 minutes of PDBu treatment (C,F) in contrast to untreated cells (B,E) or cells pre-treated with nocodazole for 2 hours before PDBu application (D,G). Arrows, podosomes. (H) Podosome numbers based on cortactin staining (similar to E–G). Data show the mean+s.e.m. (N = 40±10); *P<1×10−6 (Student's unpaired two-tailed t-test). (I) KIF1C (red) accumulates at the cell edge and podosomes (arrows). Phalloidin, green. The boxed region from the overview (upper panel) is enlarged below.