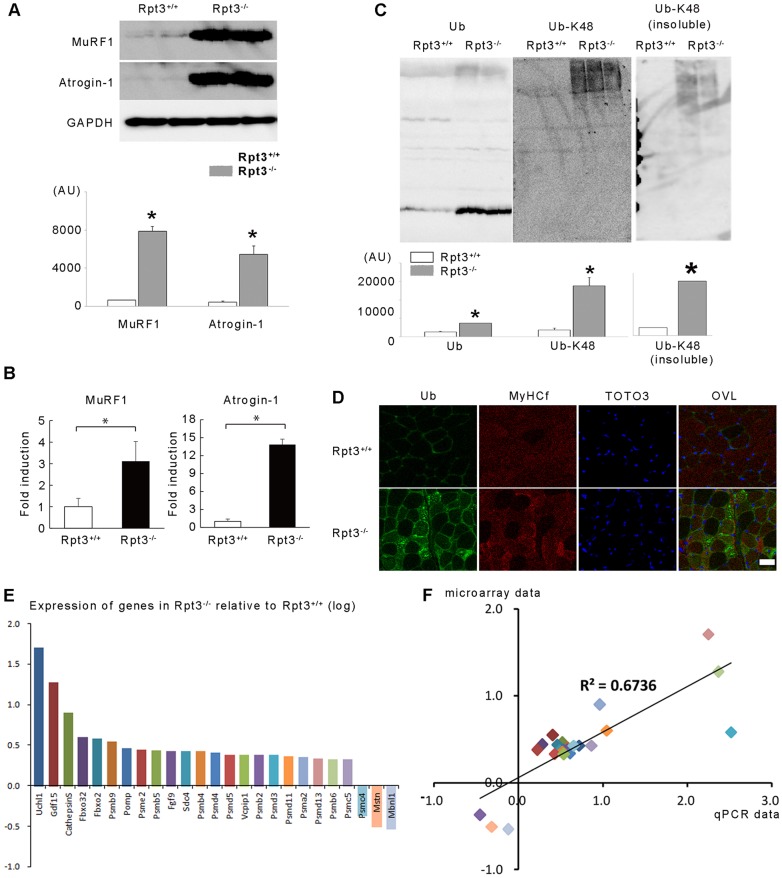
Fig. 5.
The ubiquitin–proteasome pathway is dysregulated in the gastrocnemius muscles of Rpt3−/− mice. (A) Protein levels of the muscle-specific ubiquitin-E3-ligases MuRF1 and atrogin-1 were higher in Rpt3−/− mice than in Rpt3+/+ mice at the age of 6 weeks. Quantitative data are also presented (n = 3). AU, arbitrary units. (B) Upregulation of the crucial atrophy-related and muscle-specific genes in Rpt3−/− mice at the age of 6 weeks. RNA was extracted from the gastrocnemius muscles, and quantitative PCR analysis was performed in triplicate using specific primers (supplementary material Table S1). Data were normalized to the GAPDH content and expressed as the fold increase over the expression levels in Rpt3+/+ mice (n = 5). (C) The levels of ubiquitin (Ub) and high-molecular-mass ubiquitylated proteins were increased in Rpt3−/− mice. Protein polyubiquitylated at the Lys48 residue (detected using an anti-Ub-K48 antibody) was also increased in Rpt3−/− mice. Quantitative data are also presented (n = 3). Quantitative data in A–C show the mean+s.e.m.; *P<0.05 (Student's t-test). (D) Immunohistochemical detection of ubiquitin and MyHCf revealed the accumulation of ubiquitylated proteins, particularly in fast-twitch muscle fibers. TOTO3, nuclei; OVL, overlay. Scale bar: 50 µm. (E) Upregulation of crucial proteasome-related genes in the skeletal muscles of adult Rpt3−/− mice. RNA was extracted from the gastrocnemius muscles. The y-axis represents the quantitative values of gene expression in Rpt3−/− mice relative to Rpt3+/+ mice, which were transformed to log10 values. The value ‘0’ indicates equal gene expression between Rpt3−/− and Rpt3+/+ mice. Of the several proteasome-related genes that were measured, the expression of PSMC4 (Rpt3) was inhibited in Rpt3−/− mice compared with that of Rpt3+/+ mice. Quantitative PCR analysis was performed in triplicate using specific primers (supplementary material Table S1). (F) Relative expression levels, normalized to β-actin, were well correlated between the microarray data and the quantitative PCR analysis (R2 = 0.6736).