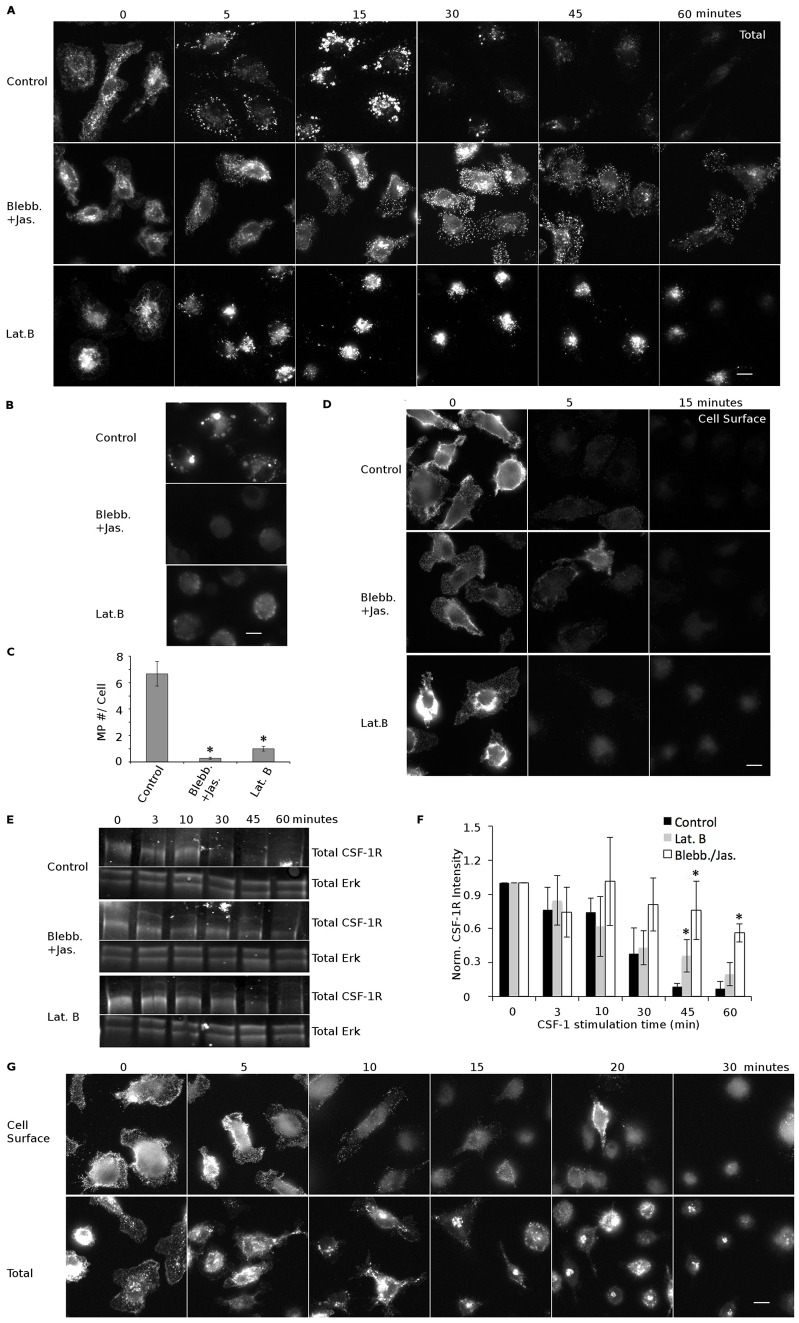
Fig. 6.
Macropinocytosis is required for efficient receptor degradation. BMMs were left untreated or were treated with blebbistatin (Blebb., 75 µM, 10-minute pretreatment) plus jasplakinolide (jas., 1 µM, 5-minute pretreatment) or with latrunculin B (Lat.B, 0.5 µM, 5 minutes) and then exposed to CSF-1 for the indicated times. (A) Images of total CSF-1R show that the receptor was redistributed to small endosomes (5 minutes) and then trafficked to macropinosomes (15 minutes) that condensed and underwent fusion (30 minutes and 45 minutes) until the CSF-1R was no longer detectable (60 minutes). Blocking macropinocytosis with blebbistatin plus jasplakinolide or with latrunculin B slowed CSF-1R degradation. Scale bar: 5 µm. (B) Treatment with blebbistatin plus jasplakinolide or with latrunculin B blocked CSF-1-induced macropinocytosis as seen by the loss of TXR–Dex uptake. Scale bar: 10 µm. (C) Quantification of macropinosome (MP) number from B. Data show the mean±s.e.m. (n = 40 cells, three experiments); *P<0.001 between control and treatments (Student's t-test). (D) Cell surface staining of CSF-1R indicates that blocking macropinocytosis does not affect receptor internalization in latrunculin-B-treated cells and causes only a small delay in blebbistatin plus jasplakinolide-treated cells. Scale bar: 10 µm. (E) Western blotting for the CSF-1R demonstrated that blocking macropinocytosis slows down CSF-1R degradation. (F) Quantification of western blots. Norm., normalized. Data show the mean±s.d. (three independent experiments); *P<0.05 between control and treatments (Student's t-test). (G) EIPA triggers receptor internalization and degradation. Cell surface CSF-1R disappeared quickly in EIPA-treated cells (40 µM, durations of pretreatment are indicated). Total receptor immunofluorescent staining demonstrated that receptor was internalized and degraded in EIPA-treated cells. Scale bar: 5 µm.