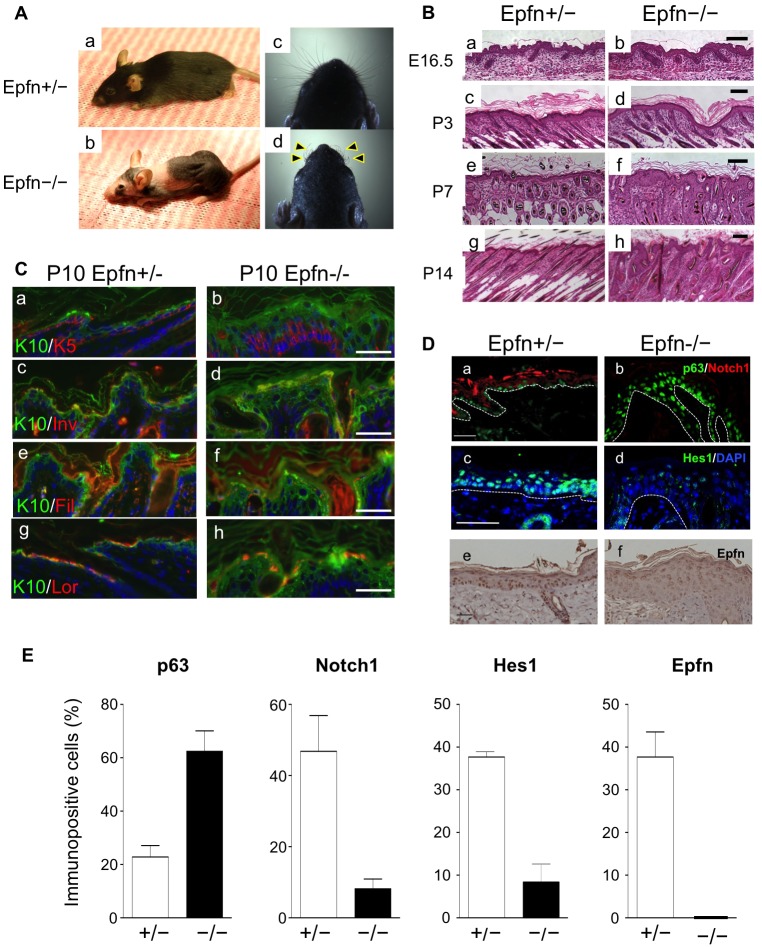
Fig. 1.
Defects of skin and hair follicle development in Epfn−/− mice. (A) Defective skin, hair follicle and whisker formation (arrowheads) in 3-month-old Epfn+/− (a,c) and Epfn−/− (b,d) mice. (B) Defective skin morphogenesis and hair follicle formation. Histological analysis of developing skin and skin morphogenesis at E16.5 (a,b), P3 (c,d), P7 (e,f) and P14 (g,h) of Epfn+/− (a,c,e,g) and Epfn−/− (b,d,f,h) mice. Scale bars: 100 µm. (C) Expression of epidermal keratinocyte differentiation marker proteins in P10 Epfn+/− (a,c,e,g) and Epfn−/− (b,d,f,h) mice. The expression patterns of K10 (green; a–h), K5 (red; a,b), involucrin (Inv; red; c,d), filaggrin (Fil; red; e,f) and loricrin (Lor; red; g,h) are shown. Hoechst 33258 (blue) was used to stain DNA (a–h). Scale bars: 100 µm. (D) The expression of p63 (green) and Notch1 (red) (a,b) in P13 mice, and Hes1 (green; c,d) in P10 mice. In P10 mice, DNA was stained with DAPI (blue). The white dotted lines indicate the basement membrane of the epidermis. Also shown is Epfn expression (DAB) (e,f) in 3-month-old mice. Scale bars: 100 µm (a,b,e,f), 50 µm (c,d). (E) Ratios of cells immunopositive for p63, Notch1, Hes1 and Epfn in the epidermis of Epfn+/− and Epfn−/− mice. Data show the mean+s.e.m. (three independent experiments).