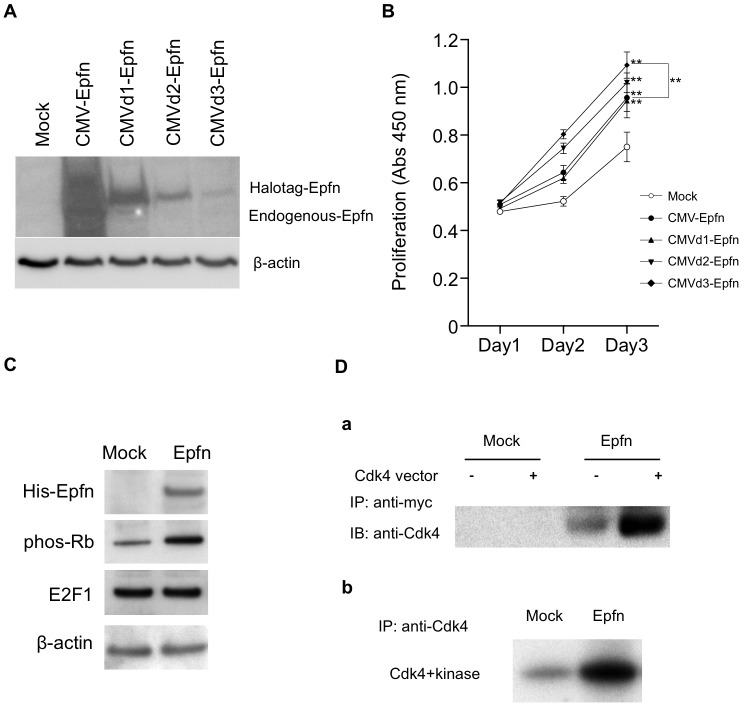
Fig. 5.
Epfn promotes HaCaT cell proliferation through enhancing Rb phosphorylation and Epfn–Cdk4 interaction. (A) Immunoblot analysis of Epfn expression in HaCaT cells transfected with various Halo-tagged Epfn expression vectors driven by either the full-length CMV promoter (CMV-Epfn) or versions of the CMV promoter containing deletions (CMVd1-Epfn, CMVd2-Epfn, CMVd3-Epfn). β-actin is shown as a loading control. (B) The relationship between Epfn expression levels and HaCaT cell proliferation. HaCaT cells were transfected with one of four Halo-tagged Epfn expression vectors. The proliferation was analyzed at various time-points. Data show the mean±s.e.m. (four independent experiments); **P<0.01. (C) Immunoblot analysis of cell cycle proteins. HaCaT cells were transfected with a His-tagged Epfn expression vector, and lysates were analyzed by western blotting using antibodies against the His tag, phos-Rb, E2F1 and β-actin (the loading control). (D) Co-immunoprecipitation assay of Epfn and Cdk4 (a) and an Rb phosphorylation assay (b) in HEK293 cells transfected with Mock or Epfn (Myc tag) expression vectors. IP, immunoprecipitated; IB, immunoblotted.