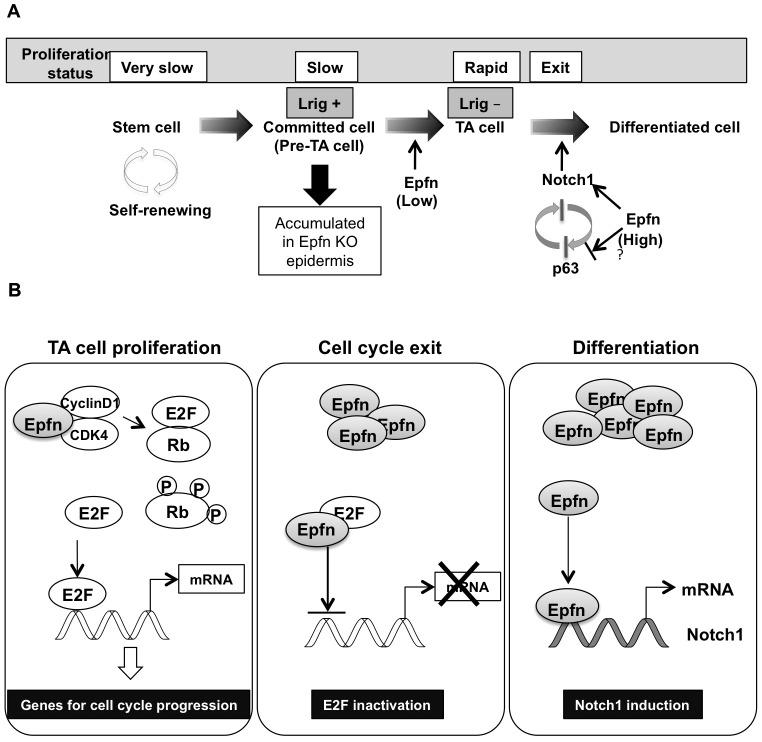
Fig. 7.
Schematic diagram of Epfn roles in keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. (A) Epfn promotes rapid transit amplifying (TA) cell proliferation. In the absence of Epfn, pre-TA cells accumulate in the epidermis. Pre-TA cells are committed to differentiation but retain some stem cell characteristics, such as slow proliferation in part due to elevated Lrig expression. As Epfn expression increases, Epfn promotes cell cycle exit and activates Notch1 expression, triggering differentiation. Epfn-induced Notch expression suppresses p63 expression. In addition, Epfn might directly inhibit p63 expression. Epfn regulates the p63 and Notch signaling pathways that are essential for epidermal development, maintenance and renewal. KO, knockout. (B) Multiple functions of Epfn during keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation. In transit amplifying cells, Epfn enhances Rb phosphorylation by interacting with CDK4 to promote proliferation. As Epfn expression increases, Epfn binds to E2F, which inhibits cell progression and promotes cell cycle exit by inhibiting E2F transactivation activity. Epfn also promotes keratinocyte differentiation by inducing Notch1 transcription.