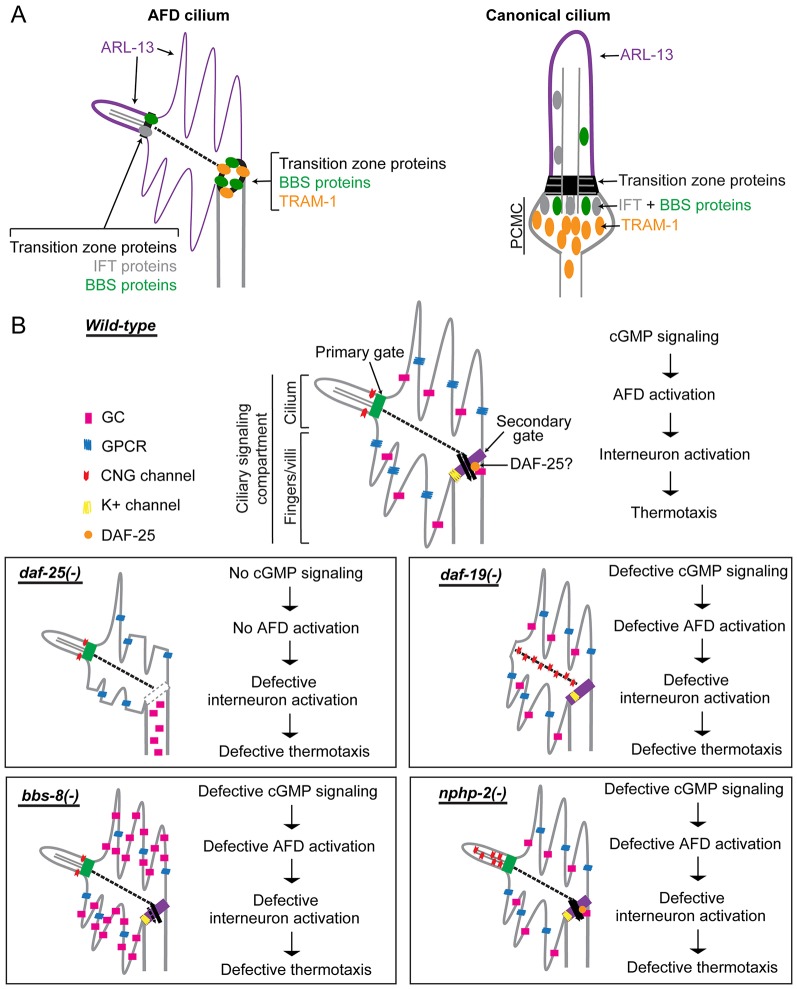
Fig. 8.
Working model of cGMP signaling compartmentalization by ciliary and other proteins at AFD sensory endings. (A) In AFD neurons, ciliary proteins are present in the cilium proper and also found at the base of the finger compartment, establishing it as a cilium-related subcompartment distinct from the periciliary membrane compartment (PCMC) found in other cilia. (B) Summary of signaling compartments in the AFD cilium of wild-type and ciliary mutant worms. DAF-25 might function at the ring structure to regulate the trafficking of signaling proteins into the finger compartment. In the daf-25 mutant, the integrity of this gate and of the fingers is compromised, and guanylyl cyclases (GC) are no longer found in the fingers, so this mutant is expected to have abrogated cGMP signaling. In the bbs-8 mutant, accumulated guanylyl cyclases in the finger compartment could result in a high basal level of cGMP, interfering with thermotransduction. In the nphp-2 mutant, the discrete CNG channel localization is disrupted, which could result in aberrant ion influx and defective neuronal activation. In the daf-19 mutant, the CNG channel is present in the non-permissive membrane environment, or becomes fixed or more abundant along the IFs, and is therefore rendered non-functional. All four mutants are predicted to have altered AFD function and are therefore defective in thermotaxis.