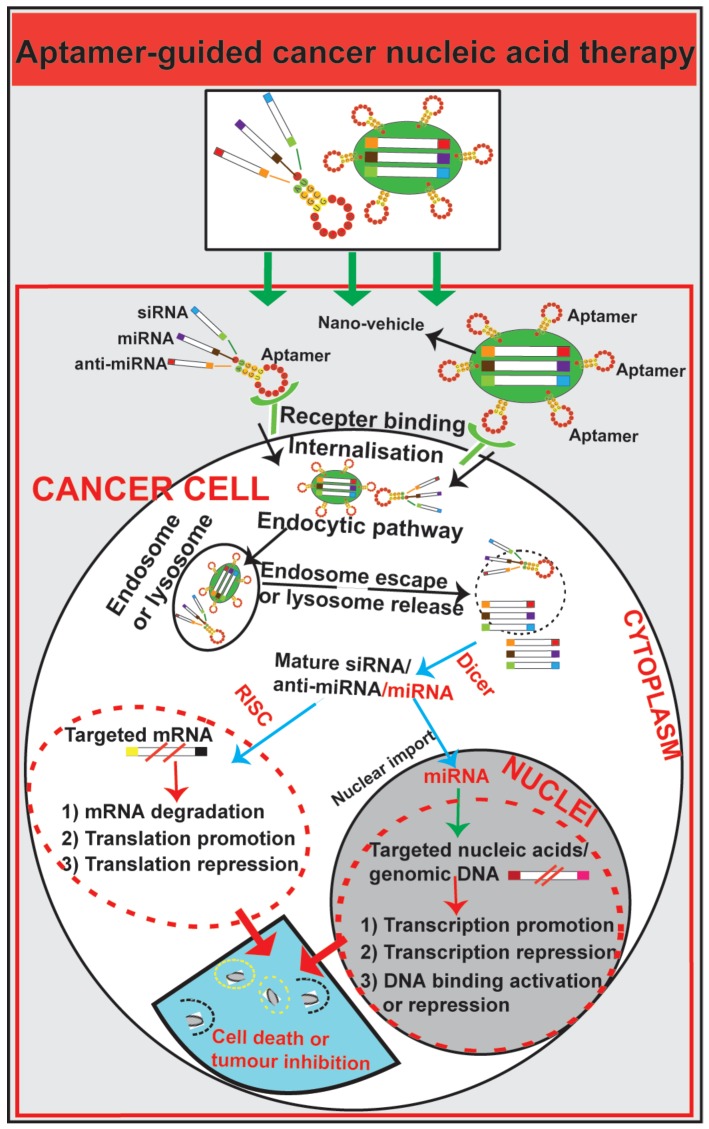
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of aptamer-guided cancer nucleic acid therapy. Exogenous therapeutic small RNAs (siRNA, miRNA and anti-miRNA) can be directly conjugated with aptamers or encapsulated within nanoparticles functionalized with an aptamer. As targeted-delivery modalities, aptamers bind to cell surface targets on cancer cells, followed by internalisation via receptor-mediated endocytosis. Through unknown mechanisms, small RNAs escape endosomes and engage cytoplasmic RNAi/miRNA protein machinery. The mature siRNA/shRNA/miRNA interact with their cytoplasmic or nucleic target sequences, leading to mRNA degradation, translation promotion or repression or modulation of gene expression.