Figure.
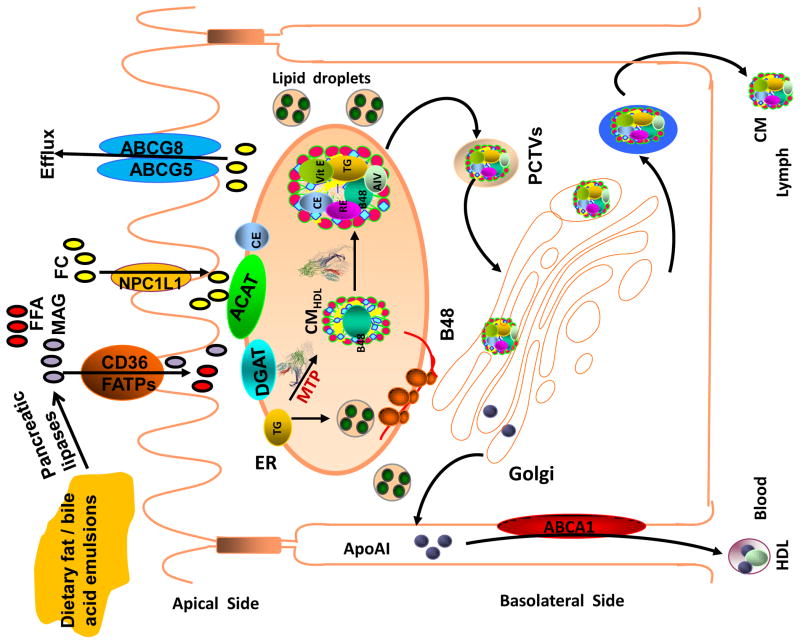
Intestinal lipid absorption: Dietary lipids are emulsified with bile salts and are hydrolyzed by different pancreatic lipases resulting in the generation of free fatty acids (FFA), monoacylglycerols (MAG) and free cholesterol (FC). These products are taken up by enterocytes involving various transporters and transported to the endoplasmic reticulum where they are used for the synthesis of phospholipids, triacylglycerols and cholesterol esters. These lipids are assembled into chylomicron particles using apoB48 as a scaffolding protein with the help of MTP. Alternatively, they are stored in cytosol as lipid droplets. FC can be either excreted back to the lumen via ABCAG5/ABCG8 transporters are effluxed to blood circulation by ABCA1 and apoAI.