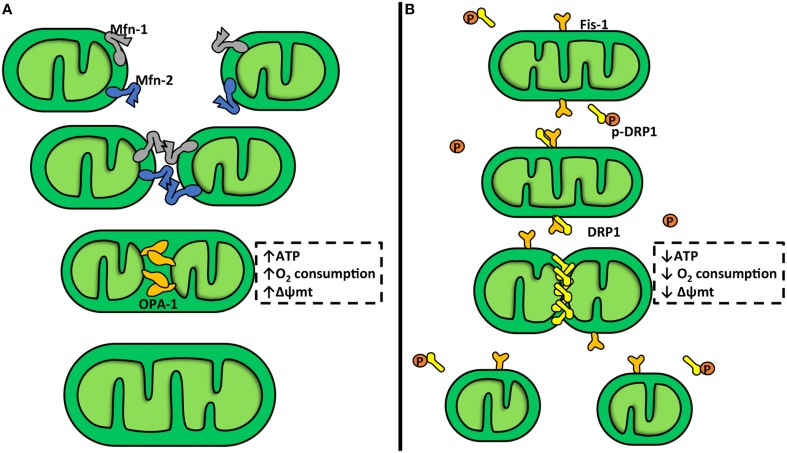
Figure 1.
Mitochondrial dynamics. (A) Mitochondrial fusion. This is a two-step process which involves three different proteins: mitofusin-1 and 2 (Mfn-1 and Mfn-2) and optic atrophy protein-1 (OPA-1). Mfn-1 and Mfn-2 are transmembrane GTPases embedded in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM). The C-terminal coiled-coil region of Mfn-1 and Mfn-2 mediates tethering between mitochondria through homo- or heterotypic complexes formed between adjacent mitochondria. This interaction mediates OMM fusion. OPA-1 is a dynamin-related protein localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM), facing the intermembrane space. OPA-1 participates in the attachment and fusion of IMM. Mitochondrial fusion is associated with an increase in the mitochondrial potential (Δψm), oxygen consumption, and ATP production. (B) Mitochondrial fission. In this process participates dynamin-related protein-1 (DRP-1) and fission protein-1 (FIS-1). DRP-1 is a large GTPase found soluble in the cytosol of cells from where it shuttles onto and off mitochondria. DRP-1 assembles into spirals at division sites around the OMM to drive the fission process. In yeast, the mechanism for recruitment of DRP-1 to the mitochondria requires FIS-1, a tetratricopeptide domain protein anchored into and evenly coating the entire OMM. DRP-1 activity is inhibited by a protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylation. Mitochondrial fission is associated with a Δψm, oxygen consumption, and ATP production decrease.