Figure 5.
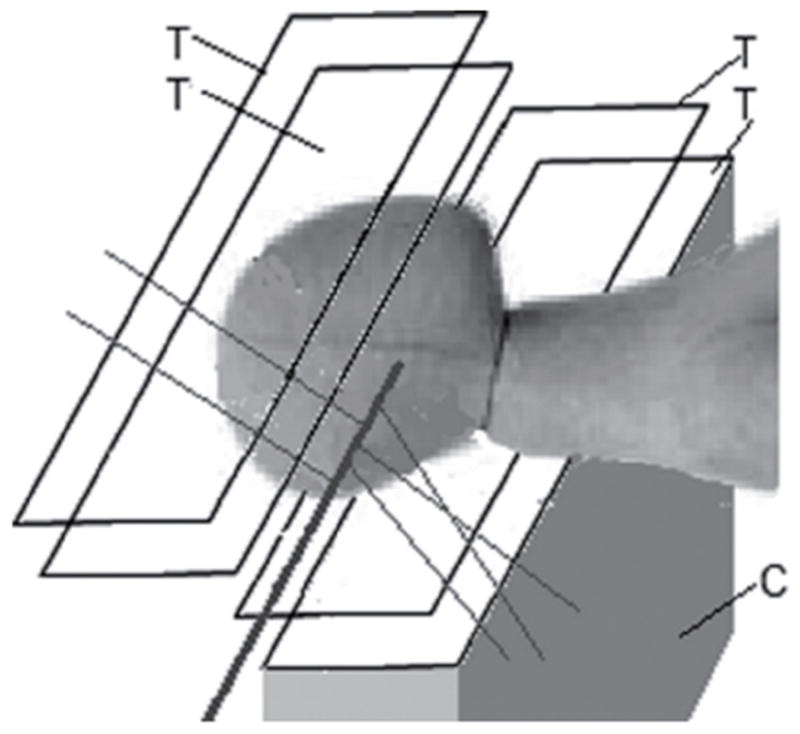
Principle of the large-angle scattered proton monitoring technique with two tracker telescopes with 4 position-sensitive planes (T). The protons scattered out of the primary beam (solid line) are detected by the trackers and their trajectory is back-tracked into the patient. The use of two telescopes increases the number of detected protons. With appropriate reconstruction techniques, the 3D position of the interaction points creating the scattered protons and thus the beam axis location can be inferred. In addition, one can also measure the energy of the tracked protons with a calorimeter (C) (here only shown in the lower half for clarity) to obtain additional data
