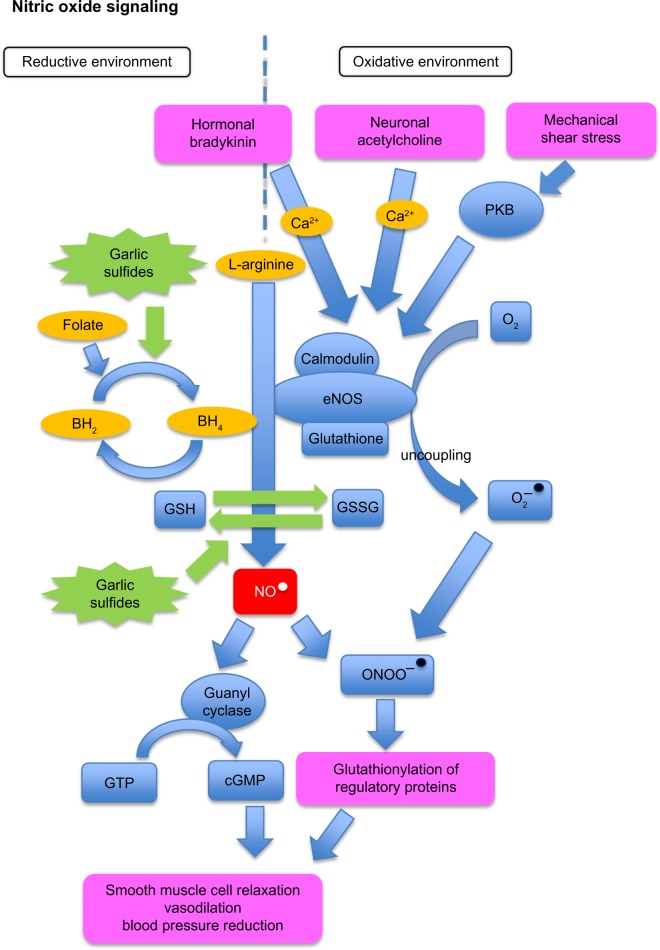
Figure 1.
Effect of garlic on blood pressure via the NO pathway.
Notes: Blue rectangles illustrate metabolites, blue circles represent enzymes, orange circles are dietary cofactors, green star shapes are garlic and other organosulfur-containing nutrients, red rectangle represents NO, and purple rectangles denote direct and indirect influence of NO on vasodilation and blood pressure. NO pathway: in the presence of BH4, eNOS produces NO, which triggers pathways leading to smooth muscle cell relaxation and vasodilation. eNOS uncoupling leads to the formation of O2−. NO and O2− combine to form OONO−, which rapidly reacts with thiols and tyrosine residues of proteins, which in turn, leads to vasodilation and BP reduction independent of cGMP. Garlic and other dietary organosulfides may play a role in the regulation of the NO signaling pathway by creating a more reductive environment and therefore supporting NO production.
Abbreviations: BH2, dihypdrobiopterin; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; Ca2+, calcium ion; cGMP, cyclic-guanosyl-monophosphate; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; eNOS, endothelial-nitric-oxide-synthase; GSH, reduced free glutathione; GTP, guanosyl-tri-phosphate; NO, nitric oxide (radical); ONOO, peroxynitrite; O2, oxygen; O2−, superoxide anion radical; PKB, protein kinase-B.